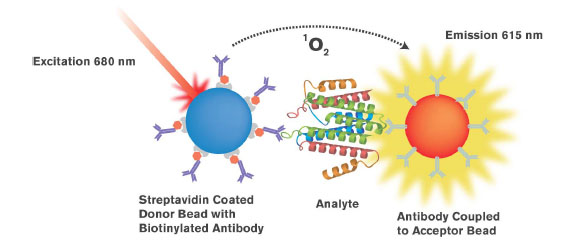
Fig. (1). AlphaScreen/AlphaLISA Assay Principle AlphaScreen/AlphaLISA assays are bead based proximity assays, based upon an oxygen channeling technology. When the Donor (blue bead), which contains phthalocyanine, is laser excited (at 680 nm) ambient oxygen is converted to singlet oxygen. This is a highly amplified reaction since approx. 60,000 singlet oxygen molecules can be generated and travel at least 200 nm in aqueous solution before decay. Consequently, if the Donor and Acceptor (gold beads) beads are within that proximity, energy transfer occurs. Singlet oxygen molecules react with chemicals in the Acceptor beads to produce a luminescent response. If the Acceptor bead contains Europium, as in the AlphaLISA assay, an intense luminescence is emitted at a wavelength of 615 nm.