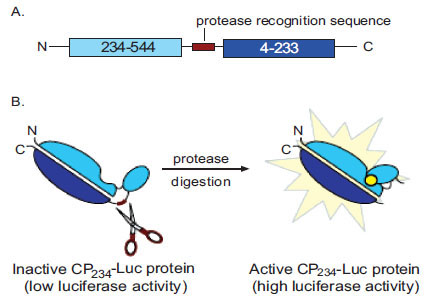
Fig. (1). Schematic Representation of the CP234-Luc Assay Firefly luciferase is a 61 kDa monomeric enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of firefly luciferin in the presence of ATP and oxygen to emit yellow-green light. Upon binding of substrates, the structure of firefly luciferase undergoes conformational changes from open to closed forms. We created a circularly permuted luciferase by covalently joining the native N and C termini of firefly luciferase through the cloning in of a short polypeptide linker containing a protease recognition sequence. This results in restricting the movement between the two domains and locking the enzyme in the less active open form. Protease cleavage releases this constriction thereby restoring higher activity. A. To express this mutant luciferase, new N and C termini were inserted at amino acids 234 and 233, respectively. B. Insertion of the polypeptide linker greatly reduces luciferase activity. Proteolytic cleavage by the cognate protease (scissors) activates the mutant luciferase enzyme resulting in a luminescent signal in the presence of the luciferin substrate (yellow circle).