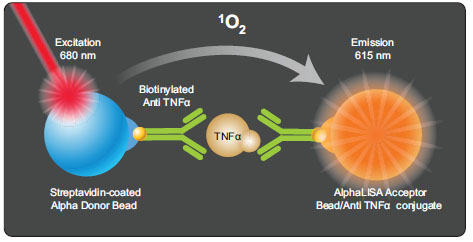
Fig. (3) Principle of AlphaLISA-based TNF-α assay. The Alpha donor bead (blue color) is coated with streptavidin which captures the biotinylated anti-TNF-α antibody. The acceptor bead (orange color) is coated with TNF-α specific antibody. When TNF-α is present, the two coated beads are brought into proximity through binding to TNF-α. After excitation by laser at 680 nm, the singlet oxygen released by alpha donor bead travels to the nearby acceptor bead where it causes acceptor bead to emit fluorescence at 615 nm. The increase of AlphaLISA signal is proportional to the concentrations of TNF-α.