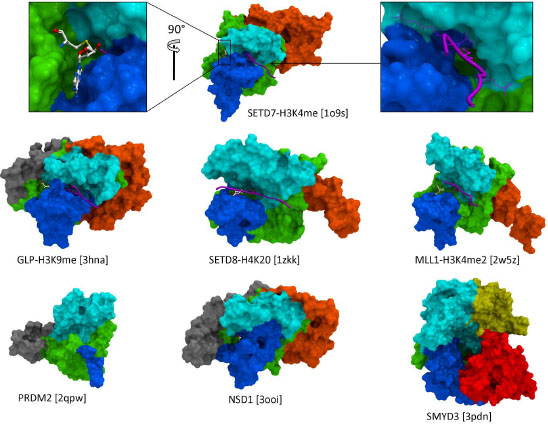
Fig. (2) Architecture of the catalytic domain. The canonical SET domain (green) includes all residues critical to catalysis. The I-SET
(cyan) and Post-SET (blue) domains are observed in all structures, and form the docking platform for the substrate peptide (magenta). The
substrate lysine inserts into a narrow channel (top right) and is shielded from solvent. The cofactor (white sticks – top left) and peptide substrate
bind at distinct druggable pockets, thereby providing multiple opportunities for chemical inhibition. Diverse combinations of N-SET
(gray), Pre-SET (orange), MYND (yellow), and CTD (red) domains can dress the core SET domain, and offer distinct interfaces to specific
interaction partners. The truncated version of the Post-SET domain observed in PRDM structures (bottom left) is probably linked to the absence
of activity of these constructs. (PDB codes are indicated in square brackets).