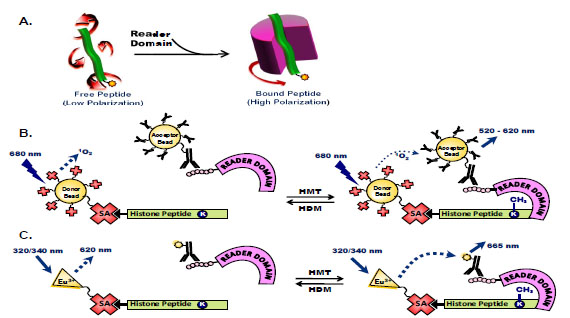
Fig. (3) Assays to measure binding of histone peptides to histone code reader domains. (A) Histone peptides tagged with a fluorescent molecule rotate freely in solution so that incident light is rapidly depolarized. Binding of chromatin-associated domains to specific posttranslational modifications of histone peptides decreases this rotational diffusion and the depolarization of light. (B) AlphaScreen assays measure peptide-protein binding of biotinylated- and methylated-histone peptides to His6-tagged chromatin-associated domains, where binding brings into close proximity streptavidin-coated donor beads and anti-His6 antibody-conjugated acceptor beads. Laser excitation of donor beads releases singlet oxygen species that excite acceptor beads to generate a chemiluminescent signal. (C) TR-FRET assays measure biotinylatedand methylated-peptide binding to His6-protein domains using donor and acceptor dyes in close proximity where the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore overlaps the absorption spectrum of the acceptor molecule. Here, Eu3+-labeled streptavidin excites anti-His6 antibody conjugated with an acceptor dye when the peptide is bound to the reader domain protein.