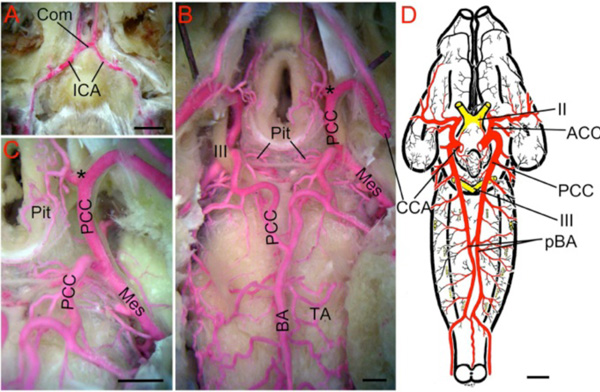
Fig. (10) Turtle. A. Ventral midline view of a red latex-filled Painted Turtle (Chrysemys picta) dissected to show the rostral-directed
internal carotid arteries (ICA) forming a short commissural crossbridge (Com) prior to entering the braincase. B. Deeper dissection showing
the cerebral carotid arteries (CCA) inside the braincase dividing (marked by black *) into the anterior (ACC; hidden from view) and posterior
(PCC) divisions. The PCC give off medially-directed pituitary branches (Pit) and large mesencephalic arteries (Mes) before joining to form a
midline unpaired basilar artery (BA). Note the location of this fusion is more caudal than in mammals, but similar to elasmobranchs. The BA
gives off a series of rhombencephalic transverse arteries (TA). C. Higher magnification view of the PCC giving off Pit and Mes arteries. D.
Brain of Geometric Tortoise (Testudo geometrica) modified after Schepers [78] showing that the PCC continue as paired basilars (pBA) that
give off transverse branches. The pBA are connected by small cross-bridges caudal to the trigeminal nerves. II, optic nerve; III, oculomotor
nerve. Scale bars are 5mm in A, 1mm in B and C, and 1cm in D.