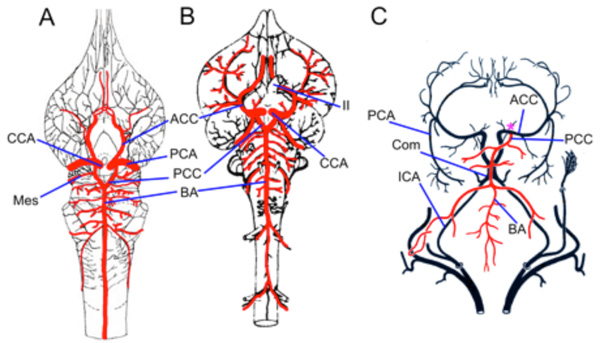
Fig. (12) Archosaurs. Illustrations of a broad-snouted caiman (Caiman latirostris, A) modified from Almeida and Campos [84] and a
chicken (Gallus domesticus, B) modified from Hofmann [13] showing the division of the cerebral carotid (CCA) into anterior (ACC) and
posterior (PCC) divisions. The PCC fuse to form a midline unpaired basilar artery (BA) that gives off transverse branches. C. Cerebral
vessels in a pigeon modified after Baumel [83] showing an unpaired BA arising unilaterally from one PCC, which is typical in most avian
groups. The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) arises from the ACC, rather than from the PCC II, optic nerve.