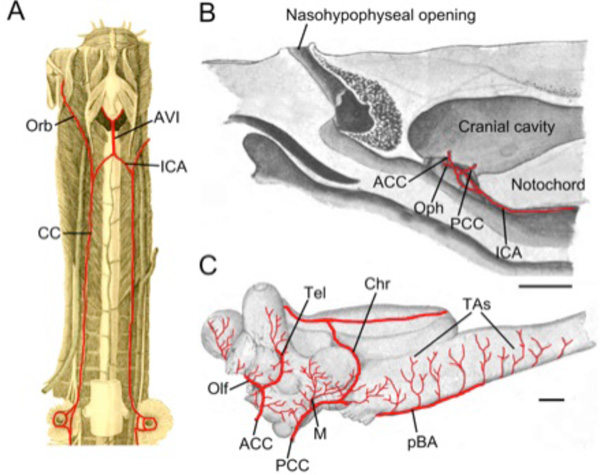
Fig. (4) Cyclostomes. A. Illustration modified after Müller [7] demonstrating the common carotid arteries (CC) traveling from the branchial
region to the cranium and then dividing into orbital (Orb) and internal carotid (ICA) arteries. The ICAs join in the midline to form an arteria
vertebralis impar (AVI). B, C. Illustrations modified after Sterzi [39] showing the cerebral vessels of the adult lamprey. B. The internal
(cerebral) carotid artery (ICA) gives off an ophthalmic (Oph) branch before dividing into anterior (ACCs) and posterior (PCCs) cerebral
carotids that enter the braincase separately, just rostral and caudal to the hypophysis. C. The ACCs give off olfactory arteries (Olfs) as well
as telencephalic arteries (Tels) to supply the forebrain. The PCCs give off mesencephalic (M) and choroidal (Chr) arteries before continuing
caudally as paired basilar arteries (pBA) that give off transverse branches (TAs). Scale bars are 5mm in B and 1mm in C.