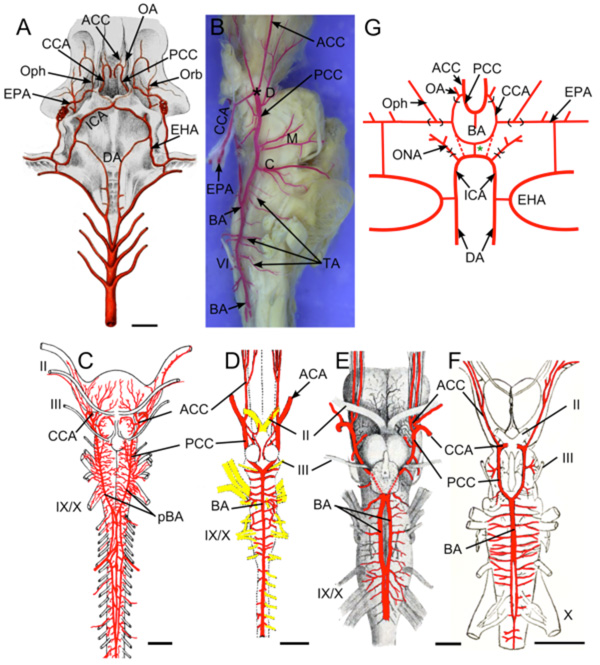
Fig. (5) Brain vasculature in Chondrichthyes . A. Arteries of spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) modified from Hyrtl [8] show paired
dorsal aortae (DA) joining the efferent hyoid arteries (EHA) which divide into internal carotid (ICA) and orbital (Orb) arteries. Paired ICA
fuse to form an unpaired carotid trunk that enters the braincase and divides into left and right cerebral carotids (CCA). Efferent
pseudobranchial arteries (EPA) give off ophthalmic arteries (Oph) before joining the CCA in the braincase. The CCA bifurcate into anterior
(ACC) and posterior (PCC) cerebral carotids. Optic arteries (OA) arise near that bifurcation. B. Lateral view of adult S. acanthias brain with
red vascular fill showing the CCA dividing (*) into ACC and PCC. The PCC give off diencephalic (D), mesencephalic (M) and cerebellar
(C) branches before fusing to form a midline basilar artery (BA) that gives off numerous transverse arteries (TA). Brain vessels of C, Raja
clavata (thornback ray) after Hofmann [13]; D, Hydrolagus colliei (ratfish) after Craigie [49]; E, Cetorhinus maximus (basking shark) after
Carazzi [42] and F, Squalus suckleyi (spotted spiny dogfish) after Daniel [48] show BA variations in different Chondrichthyes. As in most
sharks, holocephalans (D) have an unpaired BA, while skates (C) and most other batoid fish have paired basilars (pBA). Partial duplications
of the BA are shown in two elasmobranchs (E,F), likely representing variations within species that typically have a single BA. G. Schematic
of vessels in ratfish after Allis [9]. The ICA extend rostrally from the DA and give off orbitonasal arteries (ONA) before joining in the
midline. The unpaired carotid trunk (green *) and proximal part of the CCA (red dotted lines) are present in embryos and regress in adults.
The main cerebral blood supply comes from “anterior carotid” arteries (homologous to EPA of elasmobranchs) that give off ophthalmic
arteries (Oph) before entering the brain case as CCA and dividing into ACC and PCC. The PCC fuse to form an unpaired BA. II, optic nerve;
III, oculomotor nerve; IX, glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve. Scale bars are 1cm in A, C, E, F and 2.5mm in D.