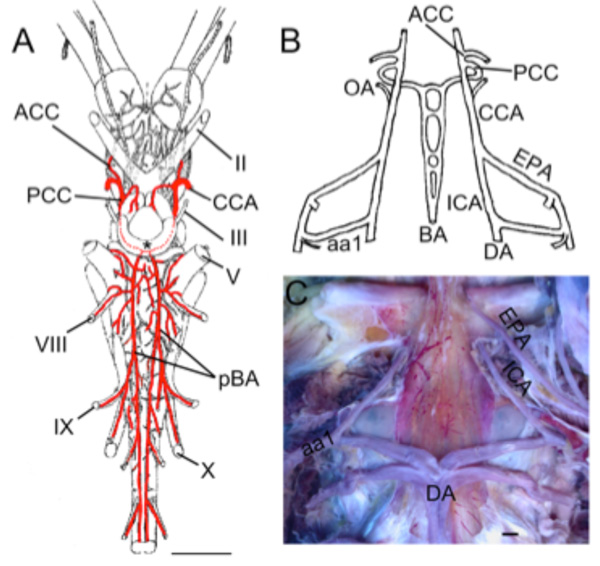
Fig. (6) Basal Actinopts. A. Illustration modified from Grodzinski [61] showing the brain vessels of Acipenser ruthenus. The cerebral
carotids (CCAs) divide into anterior (ACCs) and posterior (PCCs) divisions. The PCCs fuse to form a common crossbridge (black *) and
continue as paired basilars (pBAs). Rhombencephalic transverse branches arise from both basilars and include vessels that supply CN V,
VIII, IX, and X. B. Schematic reconstruction of larval Amia calva modified after Shearer [63] showing the internal carotids (ICAs) as rostral
extensions of the dorsal aorta (DA). The efferent pseudobranchial arteries (EPAs) join the ICAs outside of the braincase. The ICAs continue
as CCAs that give off ophthalmic arteries (OAs) before dividing into ACCs and PCCs. The PCCs in embryos and larva continue caudally as
paired basilar arteries with multiple cross bridges between them (BAs). C. Dissection of adult gar (Lepisosteus osseus) showing the paired
ICAs arising from the dorsal aorta (DA) and first epibranchial artery (aa1). The EPAs enter the braincase in close proximity to the ICAs. II,
optic nerve; III, oculomotor nerve; V, trigeminal nerve; VIII, vestibulocochlear nerve; IX glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve. Scale bars
in A, C are 2mm.