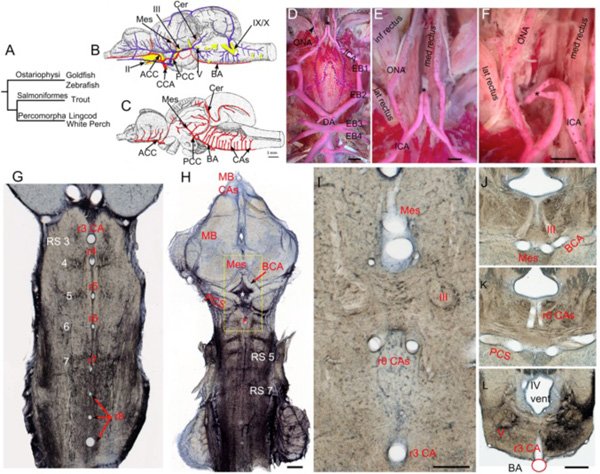
Fig. (7) Teleostean hindbrain vasculature. A. Taxonomic tree showing relationships among the teleost fish examined. B-C. Trout brain
vessels in lateral (B) and medial (C) views modified after Grodzinski [10]. The cerebral carotids (CCA) divide into anterior (ACC) and
posterior (PCC) divisions, with the paired PCC giving off mesencephalic (Mes) and cerebellar (Cer) branches before fusing to form an
unpaired basilar artery (BA). The BA gives off multiple midline rhombencephalic penetrating branches, termed central arteries (CAs). D-F.
Adult white perch (Morone americana) with red latex vascular fill showing the internal carotid arteries (ICA) extending rostrally from the
dorsal aortae (DA), giving off orbitonasal branches (ONA) and fusing to form an unpaired carotid arterial trunk (black *). The border of the
posterior part of the removed parasphenoid bone is shown by the blue dashed line. G. The segmental pattern of midline CA stems in
rhombomeres (r) 3 to r8 are shown in a horizontal section of an adult goldfish hindbrain retrogradely labeled with biocytin and
counterstained with cresyl violet. The reticulospinal neurons (RS) are located at the center of each rhombomere on either side of the CA. H.
Projection of 5 horizontal sections of the same specimen showing RS neurons and the r3 CA (red *). The caudal divisions of the ICA send
basal communicating arteries (BCA), that fuse in the midline and give off mesencephalic arteries (Mes) and posterior communicating
segments (PCS) that give off r0 CAs (white *) before fusing together to form an unpaired BA. I. High magnification view of the yellow box
in H showing the Mes, r0 CAs, and r3 CA as clear tubes. The oculomotor nerve (III) lies between the Mes and r0 CAs. J-L. Transverse
sections of another goldfish specimen show the oculomotor nerve path (J), the r0 CAs coming off the PCS (K), and the r3 CA arising from
the BA (L). II, optic nerve; V, trigeminal motor nucleus; IX, glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagus nerve; inf, lat and med rectus = inferior,
lateral and medial rectus muscles. Scale bars are 2mm in D; 1mm in E and F; 1mm in H; 250 micrometers in I; 1mm in J-L.