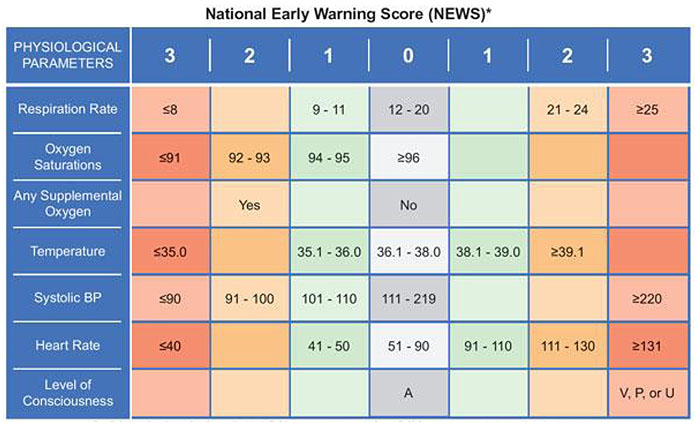
Fig. (1)
The Royal College of Physicians’ National Early Warning Score (NEWS) is based on seven easily obtained clinical parameters and produces an aggregate score between 0 and 20. It incorporates 6 vital signs as well as the AVPU scale (“alert, voice, pain, unresponsive”) used document a patient's responsiveness / level of consciousness as follows: Alert: The patient is fully awake, but not necessarily fully oriented), will spontaneously open his or her eyes, will respond to voice, and will have intact motor function. Voice: The patient makes some kind of response (via eyes, voice or movement) when you talk to them, although the response could be as little as a moan, or slight limb movement. Pain: The patient makes a response (again, via eyes, voice or movement) following the application of noxious stimulus, such as sternal rub. Unresponsive: The patient provides no eye, voice or motor response to either voice or pain. Note that a new onset of confusion merits clinical evaluation even if it is not formally part of the NEWS system. Patients are at “low risk” with aggregate scores 4 and under, at “medium risk” with aggregate NEWS scores of 5 or 6 or if an individual parameter scores at 3, and are at “high risk” with aggregate NEWS scores exceeding 6. From: https://www.rcplondon .ac.uk/sites/default/files/ documents/national-early-warning-score-standardising- assessment-acute-illness-severity-nhs.pdf