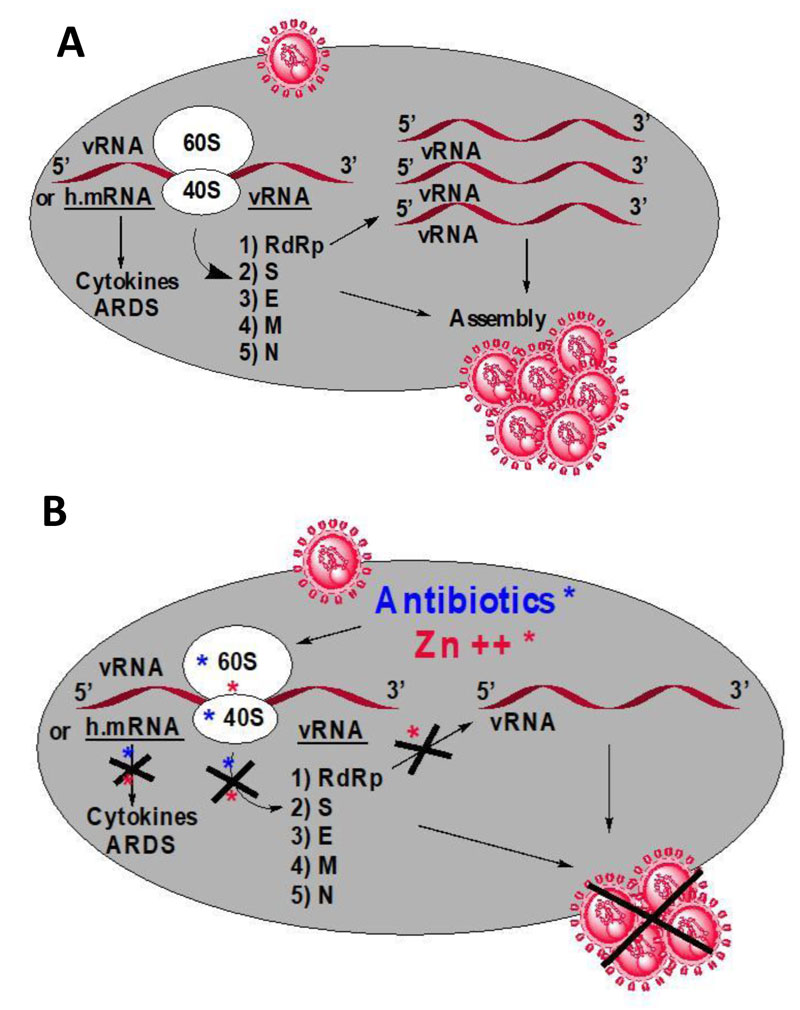
Fig. (1)
Schematic view of a SARS-CoV-2-infected human cell in the absence or the presence of small-molecule inhibitors. (A) Following the entry of the virus into the host cell, the viral RNA genome (vRNA) is released in the cytoplasm and binds to the human 80S ribosome (composed of the 40S and 60S subunits) which is in charge of translating the viral enzymes and proteins in the order of 1) 5′ RNA replicase (ORF1a/b) (an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, RdRp) -structural proteins [2) spike (S) - 3) envelope (E) - 4) membrane (M) - 5) nucleocapsid (N)] -3′ [3]. RdRp catalyzes the synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to the viral RNA genome as a template. Thereafter, assembly of a copy of the viral genome and of the RNA replicase as well as of the structural proteins reconstitutes new viral particles. Cytokines are proteins synthesized by the ribosomes of the infected host cells using the human mRNA (h.mRNA) as a template, and glycosylated post-translationally by human glycosylases. These glycoproteins (IL-1, IL-6, etc) are responsible of the so-called cytokine release storms, the hyperinflammation process leading to the COVID-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); (B) adequate antibiotics (blue star) are capable of inhibiting the human 80S ribosomes of the SARS-CoV-2-infected cells in order to prevent them from producing for the virus the proteins and enzymes essential to its replication and/or to the assembly of viral particles. In addition, the antibiotics are also capable of preventing the synthesis from the h.mRNA of the cytokines, the glycoproteins (IL-1, IL-6, etc) responsible of the so-called cytokine release storms, the hyperinflammation process leading to the COVID-related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Finally, it was previously demonstrated that Zn++ (red star) exhibits the following inhibitory activities: (i) it inhibits the RdRp and prevents the replication of the viral RNA genome of SARS-CoV-2; (ii) it inhibits translation initiation thus preventing the global synthesis of all viral proteins and enzymes including the RNA replicase responsible for the replicative cycle of SARS-CoV-2; (iii) it increases anti-inflammatory activities by suppressing the formation from the h.mRNA of the cytokines through inhibition of translation initiation.