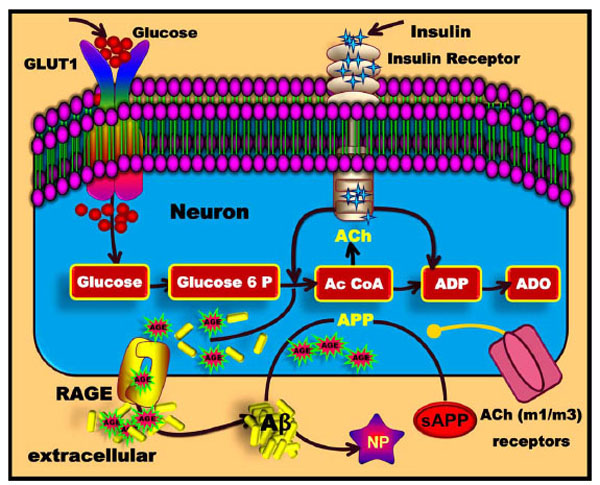
Fig. (6) Formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetic vascular diseases and AD. Glucose enters the cell and the glycolytic and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) pathways and eventually produces ATP and amino acids. AGEs are formed from reactions between carbohydrates and proteins. Subsequently, AGEs bind to the RAGE receptors. The RAGE receptor helps Aβ to cross the BBB, after which Aβ forms neuritic plaques (NP).