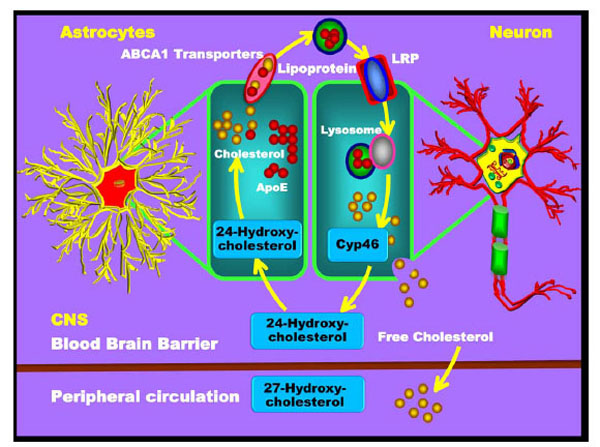
Fig. (8) Cholesterol transport and metabolism in the brain. Cholesterol is mainly generated in astrocytes and is then transported to neurons. Cholesterol and ApoE are synthesised by the astrocytes and form the lipoprotein compound. These lipoproteins enter neurons through the neuronal surface receptors of the LDL-receptor related protein (LRP). Upon neuronal entry, the lysosome reacts with the lipoprotein and releases the free cholesterol from the neuron. Some of the free cholesterol reacts with the Cyp46 enzyme and forms the 24-hydroxycholesterol. The 24-hydroxycholesterol is then released from the neuron to enter the astrocytes and to be reconverted into cholesterol. The remaining free cholesterol released from neurons crosses the BBB into the peripheral blood circulation.