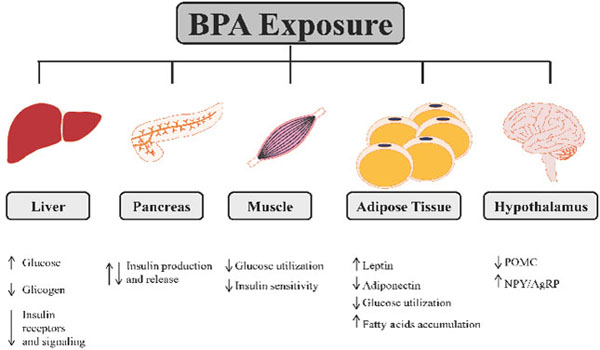
Fig. (1)
BPA exposure may lead to metabolic dysfunction affecting glucose homeostasis at different levels involving the main tissues that control glucose homeostasis. BPA increases glucose production and reduces glycogen synthesis in liver with a reduction of glucose oxidation and impairment in insulin signaling. In pancreas BPA modulates positively or negatively insulin production and release. In muscles BPA is able to decrease glucose utilization and insulin sensitivity. White adipose tissue endocrine function is modulated by BPA affecting leptin and adiponectin secretion, reducing glucose utilization and increasing fatty acids accumulation. Hypothalamus can be affected by BPA disruption regulating POMC and NPY/AgRP expression in the arcuate nucleus.