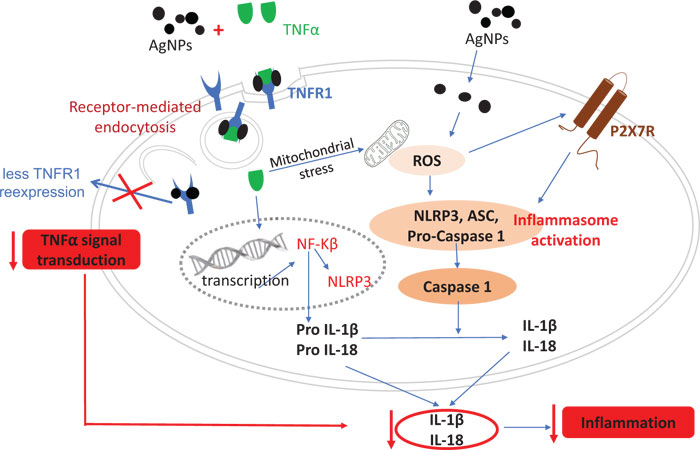
Fig. (7) Molecular mechanism explaining two different possible pathways (TNFR1 and P2X7R) that can reduce the TNFα-induced inflammatory response by AgNPs. Arrows show signal transductions. The red arrows show the reduction of the TNFα-induced inflammatory response. In case of exposure to both TNFαand AgNPs, the nanoparticles non-specifically bind to TNFR1, and TNFα binds specifically with the same receptor, forming a TNFR1-TNFα-AgNPs complex which then enters the cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. TNFα is then released from the receptor and induces the inflammatory response. The receptors might still bind to AgNPs, thus disturbing the receptor’s shape, molecular weight, and characteristics, leading to disturbance of its normal pathway of being recycled to the cell membrane, resulting in less TNFR1 on the cell membrane and more inside the cells.