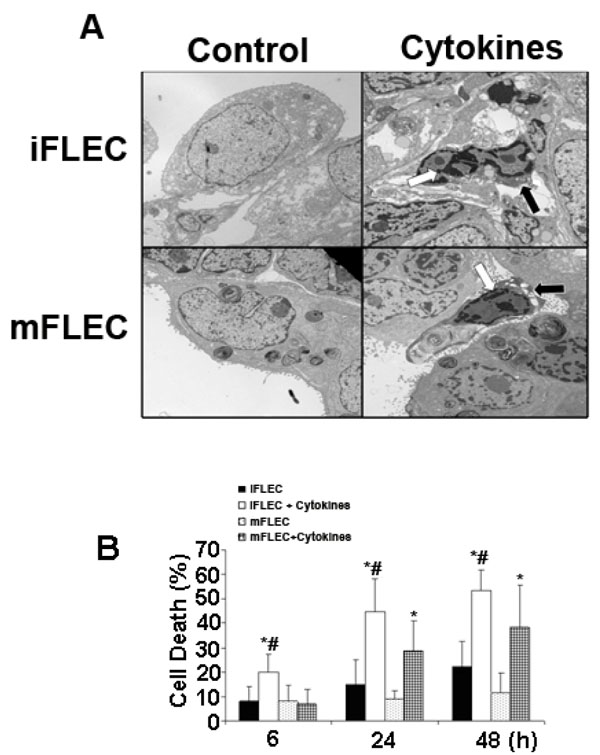
Fig. (1) Cytokines induce apoptosis of human fetal lung epithelial
cells. (A) Electron Microscopy of immature and mature human fetal
lung epithelial cells incubated with or without cytokines for 24
hours. The presence of abundant multi-vesicular bodies
differentiates immature from mature human fetal lung epithelial
cells. Nuclear (white arrows) and cytoplasmic (black arrows)
condensation present in cytokine-stimulated immature and mature
human fetal lung epithelial cells (bar=10µm). (B) Percentage of cell
death in immature and mature human fetal lung epithelial cells
upon cytokine exposure. Cytokine exposure resulted in an increase
in cell death in immature human fetal lung epithelial cells and in
mature human fetal lung epithelial cells at 24 and 48 hours
(*p<0.05). Cytokine-exposed immature cells had a more rapid and
increased degree of cell death compared to cytokine-exposed
mature cells (#p<0.01).