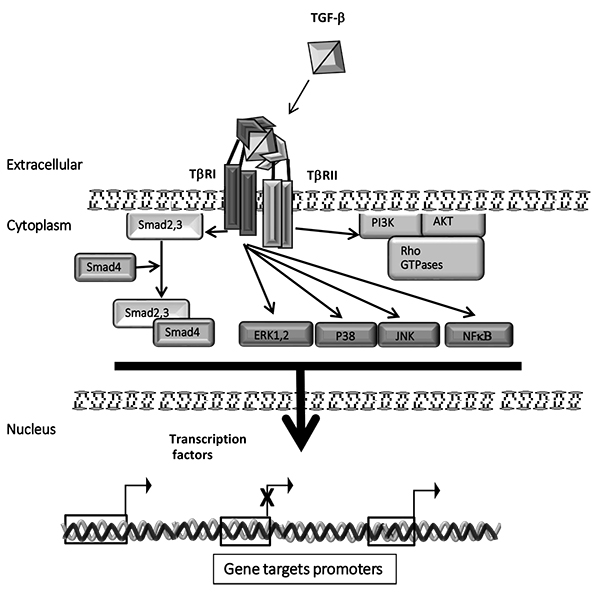
Fig. (1) TGF-β1 intracellular signaling. TGF-β1 signalizes through interaction with TGF-β1 receptor-type II (TβRII) and subsequently with TGF-β1 receptor-type I (TβRI). The activated ligand and receptors complex proceeds to the activation by phosphorylation of the canonical effectors Smad2 and Smad3 that then forms a heteromeric complex to translocate into the nucleus and mediate the regulation of the genes target expression. Furthermore, TGF-β1 is able to activate several non-canonical intracellular signaling including MAP kinases (ERK1,2, p38 and JNK), NF-κB, PI3 kinase pathways, and small Rho GTPases, among others. The canonical and non-canonical signal transductions together regulate many of the cellular and molecular functions of TGF-β1.