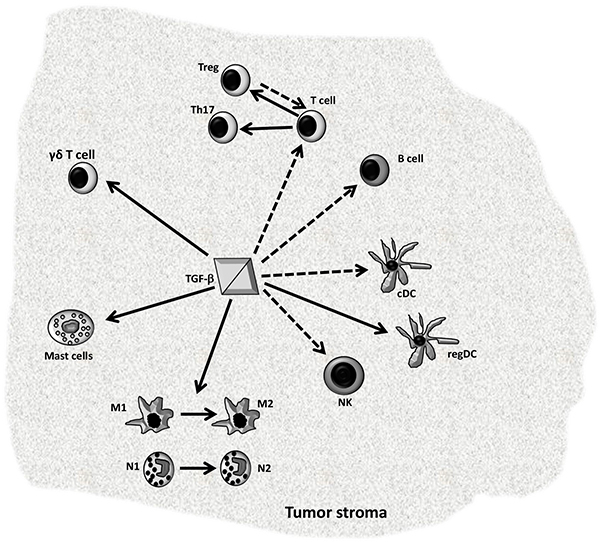
Fig. (2) Overview of TGF-β1 regulation of immune system. TGF-β1 as a potent immune-suppressive cytokine regulates many cellular components of the immune system. TGF-β1 inhibits the activation and function of T lymphocytes (T cell) and induces them to differentiate to Tregulatory (Treg) and Th17 phenotypes. Also, it inhibits B lymphocytes (B cell) proliferation, classical dendritic cells (cDC) maturation and natural killer (NK) functions. Furthermore, TGF-β1 promotes the switch of tumor-associated macrophages M1 and neutrophils N1 towards M2 and N2 respectively. Also, TGF-β functions as chemotactic factor for mast cells, as well as it contributes to the generation of γδ T cells and regulatory DC (regDC). By these regulations, TGF-β1 induces an immune-permissive tumor stroma that contributes to the tumor progression. Dotted line arrows indicate inhibition and solid line arrows indicate induction.