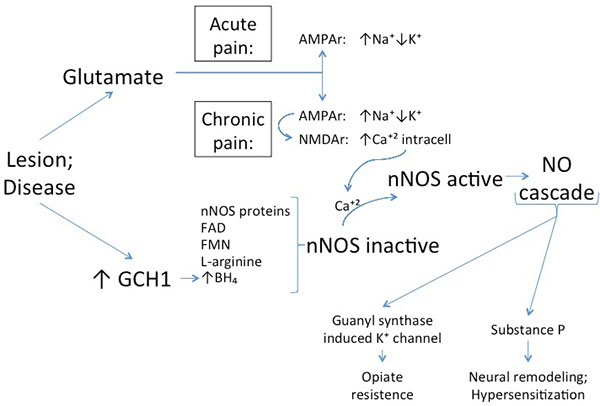
Fig. (3) Nociceptive sensitization related to NO/ROS cascade. Neurotransmitter glutamate is secreted from the nociceptor terminal to the synaptic cleft and sensitizes AMPA receptors (AMPAr) on dorsal horn cells membrane. In long-term, the changes in membrane polarization affect the NMDA receptors (NMDAr). NMDAr sensitization allows the Ca+2 influx, which is essential to the neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (nNOS) activation. The nNOS activation is possible only if the inactive nNOS has all the cofactors (FAD, FMN, L-arginine and BH4) dimerized. For this, a lesion also increases the GTP cyclohydrolase (GCH1) levels, enhancing BH4. Ultimately, NO produced in the dorsal horn cells are released back into the synaptic cleft for closing guanyl synthase-induced K+ channels and for releasing Substance P. Respectively, the results are the opiate resistance in chronic pain and neural remodeling and hypersensitization.