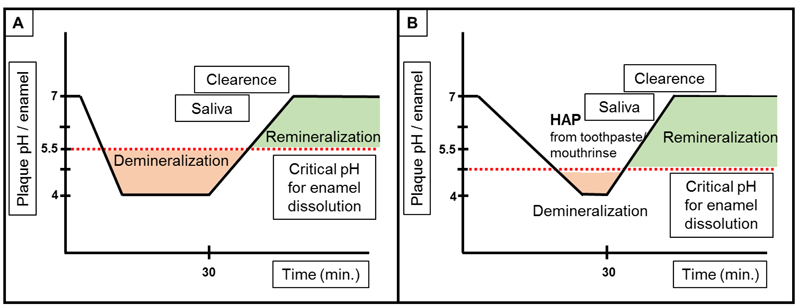
Fig. (6) (A) shows a caries attack in the absence of HAP. The natural tooth will get demineralized at a pH around < 5.5. After a certain time, saliva will clear the acids and salivary ions will lead to a (partial) remineralization of the enamel. (B) shows the same conditions, but in the presence of extrinsic HAP (from toothpaste or mouth rinse), the dissolution of the natural enamel is decreased. Due to the presence of HAP, and a change of the solubility equilibrium, the natural enamel will be protected [115, 116].