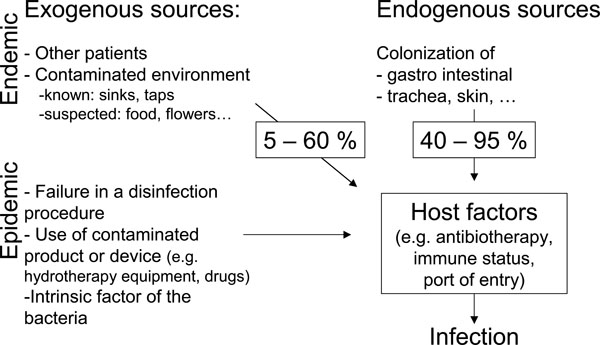
Fig. (1) Schematic representation of the factors contributing to the epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Intensive Care Units. Other patients or contaminated environment are potential exogenous sources of infections. Failure in a disinfection procedure, the use of contaminated product or device are often cited as the source of epidemics. Intrinsic factors of the bacteria (e.g. multidrug-resistance) might also play a role in epidemics. On the other hand, colonization of the gastro-intestinal track, the trachea or the skin are the major endogenous sources of infections. Infections in the patients will occurred only if an opportunity is given to the pathogen (e.g. antibiotic therapy, immuno-supression, port of entry).