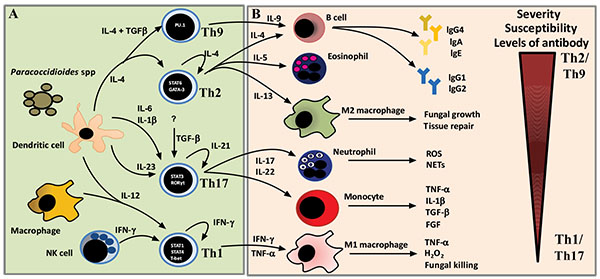
Fig. (4)
Overview of the polarization of adaptive immune in PCM.(A) Activation of T helper (Th) subsets. Paracoccidioides antigen-primed dendritic cells (DCs) migrate to the lymph node where they present processed antigens to naïve Thcells that differentiate into one of Th lymphocyte subsets (Th1, Th2, Th9 and Th17) depending primarily on cytokines present in the extracellular environment. For Th1 polarization, IL-12 from DCs and macrophages, and IFN-γ from NK cells activate STAT1/STAT4 signaling to induce expression of the Th1-specific transcription factor, T-bet. For Th17 polarization, IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β and IL-23 are required to induce expression of the Th17-specific transcription factor, RORβτ, through STAT3 signaling. For Th2 polarization, IL-4 from DCs activates STAT6 signaling to induce expression of the Th2-specific transcription factor, GATA-3. For Th9 polarization, IL-4 and TGF-β are required to induce expression of the Th9-specific transcription factor, PU.1. (B) Effector phases of T cell responses. Th1, Th17, Th2 and Th9 clones could be distinguished mainly by the cytokines produced by the cells. Th1 cells release high amounts of IFN-γ and TNF-α that classically activate macrophages (M1) resulting in fungal elimination. Th17 cells secrete IL-17 and IL-22 that recruit neutrophils and monocytes. Neutrophils cells act by generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) that result in fungal elimination. Monocytes have been studied in PCM by induce high levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, and growth factors, such as TGF-β and fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Th2 show several functions that depend of each secreted cytokine. IL-4 induces activation of B cells and subsequent production of immunoglobulins; IL-5 triggers recruitment of eosinophils; and IL-13 is involved in the deactivation of macrophages, termed “alternatively activated macrophages” (M2), that results in fungal growth and also in tissue repair. Th9 release IL-9 and IL-21 that act in synergy with Th2 to produce antibodies.