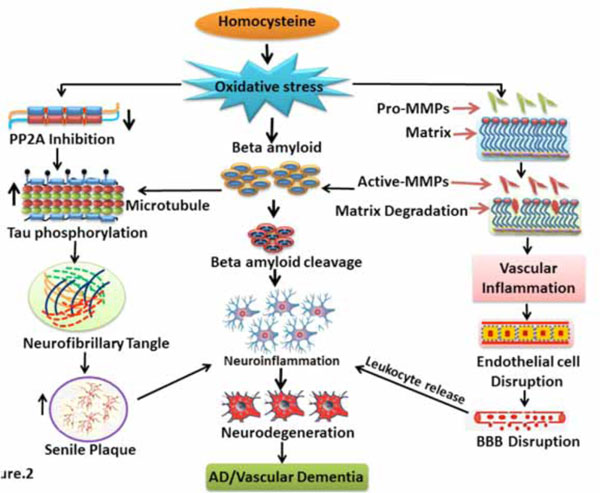
Fig. (2) Homocysteine and Vascular Dementia: Flow diagram showing the mechanism of homocysteine induced vascular dementia.
Homocysteine produces oxidative stress in the initial stage. Further oxidative stress leads to activation of MMPs as well as PP2A inhibition.
Activated MMPs promote matrix degradation, vascular inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and finally BBB dysfunction. Activated
MMPs may also promote beta amyloid (Aβ) cleavage and neuroinflammation. PP2A inhibition by homocysteine causes Tau
hyperphosphorylation. These events result in the neurofibrillary and senile plaque formation in the brain. Further, senile plaque and
neurofibrillary tangle formation promotes neurodegeneration and thus initiates AD and vascular dementia like symptoms.