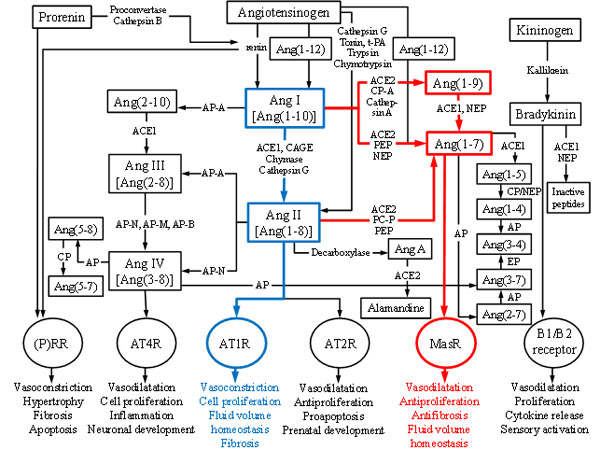
Fig. (1) The renin-angiotensin system. The two main axes of RAS are highlighted with colors. ACE2-Ang(1-7)-MasR axis (red lines) counterbalances the harmful effects of the ACE1-Ang II-AT1R axis (blue lines). ACE1: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 1; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme related carboxypeptidase; Ang I, II, III, IV: Angiotensin I, II, III, IV; Ang A: Angiotensin A; AT1R, -2R, -4R: Angiotensin II type 1, -2, -4 receptor; AP: Aminopeptidase (-A, -N, -M, -B); B1/B2: Bradykinin receptors; CAGE: Chymostatin-sensitive Ang II generating enzyme; CP: Carboxypeptidase; EP: Endopeptidase; Mas receptor: Ang(1-7) receptor type; NEP: Neprilysin; PEP: Prolyl-endopeptidase; PCP: Prolyl-carboxypeptidase; tPA: Tissue-type plasminogen activator. In angiotensin peptides the numbers in parenthesis refers to the numbers of amino acid residues. The figure is updated from Vaajanen et al. [41].