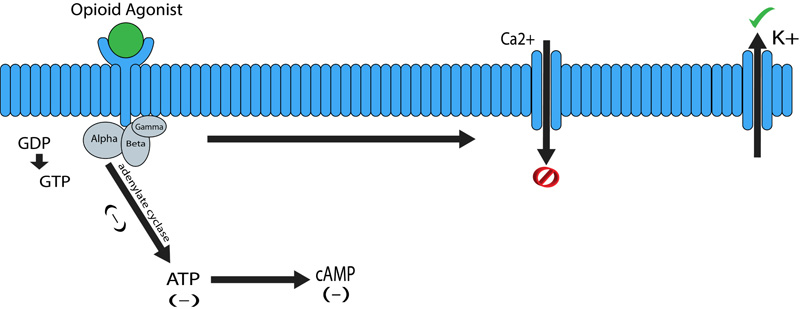
Fig. (2)
Opioid G-protein-coupled mechanism of action. Binding of the opioid agonist to the receptor causes the α subunit of the G-protein, intracellularly exchanges its bound guanosine diphosphate (GDP) molecule with the guanosine triphosphate (GTP). This separates the two complexes α-GTP and βγ complex. The α-GTP complex interacts with adenylate cyclase causing the intercellular levels of cAMP to drop. These complexes also interact with ion channels, inhibiting the flow of Calcium and upregulating the flow of potassium, causing the cell to hyperpolarize, thereby reducing conductance and relay of information.