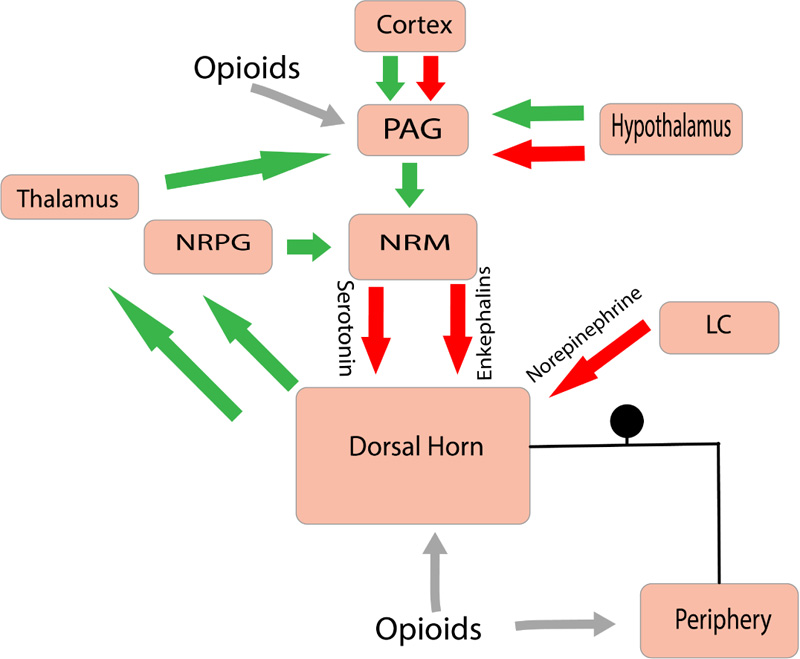
Fig. (3)
The opioid mediated analgesic pathway. The way the mu-opioid receptor agonist work is by activating the descending inhibitory pathway that acts upon the PAG along with Nucleus Reticularis Paragigantocellularis (NRPG). Because of this the descending inhibitory neurons are activated, causing a massive increase in the neuronal transmission into the Nucleus Raphe Magnus (NRM). This leads to upregulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine and enkephalin-containing neurons that innervate the substantia gelatinosa of the dorsal horn. The net inhibitory effect causes reduction of nociceptive information from the peripheral receptors to the thalamus. Green arrows represent excitatory effect while the Red arrows represent an inhibitory effect.