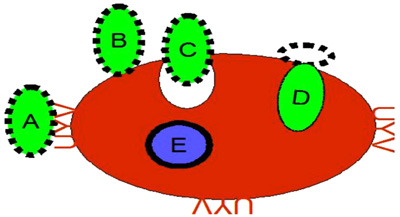
Fig. (2) Erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium merozoite. A- Merozoite attachment. Reticulocyte Binding-Like Family (RBL) proteins play a major role in the
mechanisms of invasion of erythrocyte and reticulocyte. They are several parasitic ligands such as
the high molecular mass Rhoptry Protein (RHOP-H), the Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry neck
protein (PfAARP), the Serine Repeat Antigen (SERA), the Mature parasite-infected Erythrocyte
Surface Antigen (MESA), the Erythrocyte Binding Antigen (EBA) and the Merozoite Surface Protein
(MSP-1). Plasmodium ligands bind multiple receptors on the membrane of the erythrocyte such as
spectrin, band 3, actin, glycophorin, band 4.1, band 4.2, aquoporin-1, band 7 and ankyrin. B- Merozoite
reorientation and junction formation. C- Parasitophorous vacuole formation and invasion.
D- Pinching off the junction and shedding of surface coat. E- Ring stage.