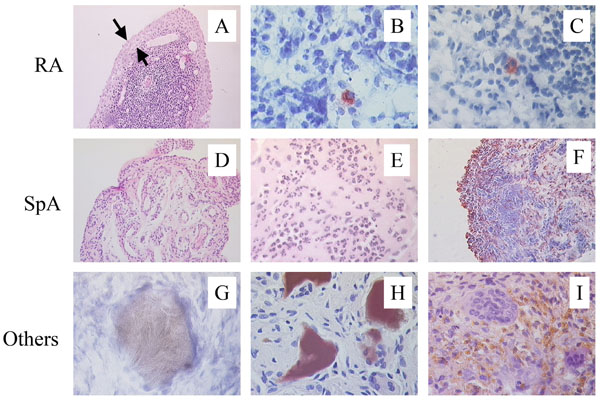
Fig. (1) Distinct features of SpA synovitis. In comparison with RA, SpA synovitis displays less synovial lining layer hyperplasia (A), the abcens of intracellular citrullinated proteins (B), and the absence of HLA-DR4/HC gp-39 peptide complexes (C). Vascularity (D) as well as infiltration with polymorphonuclear cells (E) and CD163+ macrophages (F) is clearly increased in SpA. Depositions of uridic acid crystals (G), homogentisic acid (H), and hemosiderin (I) are typical for gout, ochronosis, and pigmented villonodular synovitis, respectively, and are not found in SpA synovitis.