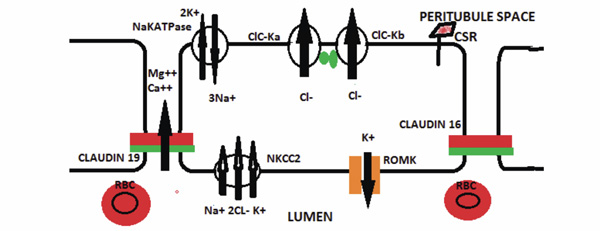
Fig. (3) Hereditary Disorders of the Thick Ascending Limb Cell. The major hereditary disorder of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle
is Bartter syndrome which can be caused by a number of mutated proteins. An abnormality in the NKCC2 protein impairs sodium,
potassium, and chloride reabsorption from the lumen. A mutated ROMK protein can also cause Bartter syndrome by impairing potassium
recycling for the NKCC transporter. Bartter syndrome can also be caused by a mutated CIC-Kb, Barttin ( ), or both CIC-Ka and CIC-Ka. A
mutated calcium sensing receptor (CSA) that is constitutively on can cause Bartter syndrome by down-regulating the NKCC2 in association
with hypocalcemia. Impaired luminal calcium absorption causes decreased paracellular calcium absorption and hypercalciuria. Familial
hypomagnesemia, hypercalciuria with nephrocalcinosis syndrome is caused by either a mutated claudin 16 or 19 protein that impairs
paracellular calcium and magnesium absorption.