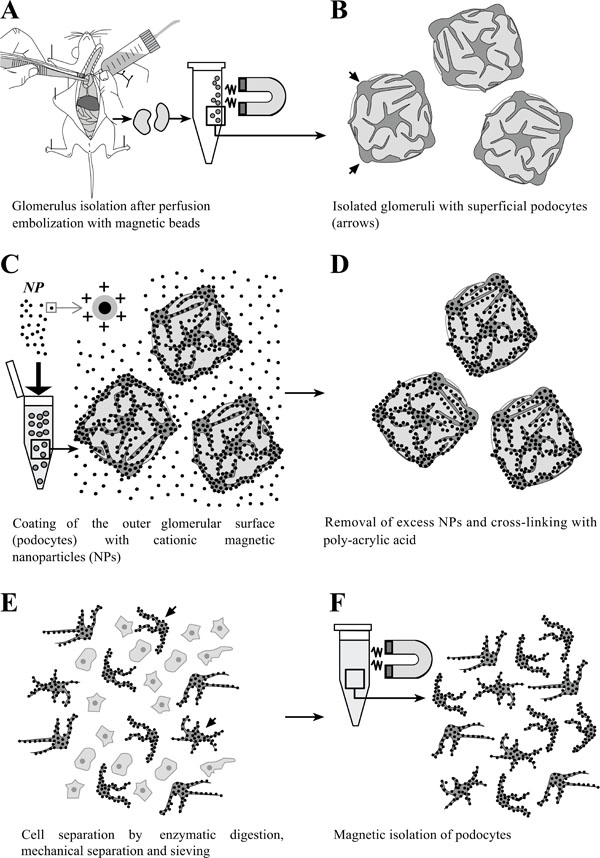
Fig. (1)
Schematic illustration of the
principle of isolation of podocytes coated with cationic colloidal
silica-coated ferromagnetic nanoparticles (NPs). A:
Glomeruli are isolated after perfusion with spherical superparamagnetic beads.
B: Simplified schematic illustration of isolated glomeruli. Podocytes
residing on the outer glomerular surface are indicated by arrows. C:
Incubation of isolated glomeruli with NPs, binding to the exposed negatively charged podocyte cell surfaces. D:
Excess NPs are removed from the sample by sieving. Podocyte-bound NPs are cross-linked by addition of
poly-acrylic acid, simultaneously neutralizing the exposed surfaces of NPs to avoid binding to other cell types after
cell separation. E: Glomerular cells are dissociated by enzymatic digestion, gentle mechanic squeezing in a Dounce
tissue grinder, and subsequent sieving. F: Isolation and repeated washing of NP-coated podocytes in a magnetic
field.