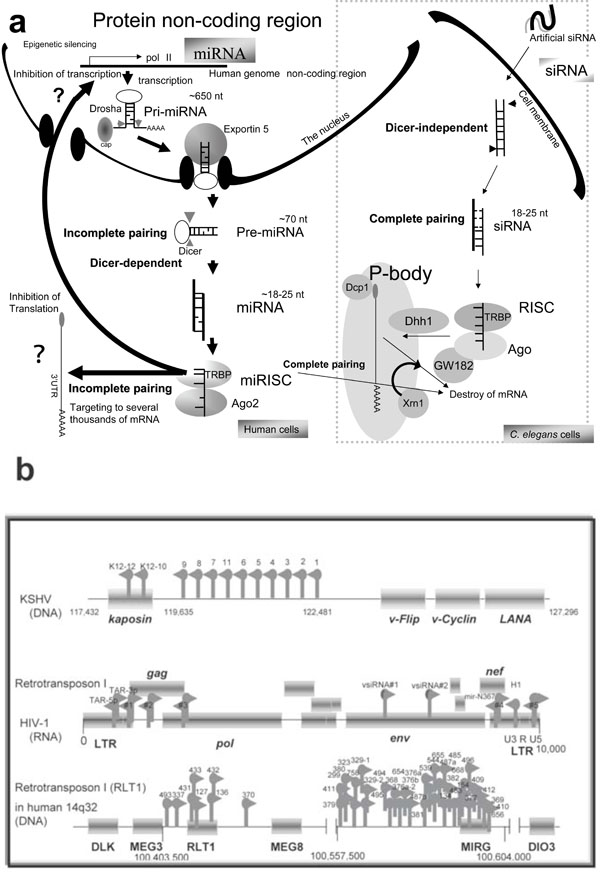
Fig. (1) Human miRNA biogenesis and its sources. (a) Human miRNA genes are hidden in the protein non-coding regions and pri-miRNA involves from a long transcript precursor, which can be generated by Pol II or Pol III RNA promoters. The intronic miRNAs are transcribed by the Pol II promoters of the protein-coding genes. In the nucleus, the pri-miRNA is excised by Drosha RNase and the processed pre-miRNA is transported by Expotin-5 to the cytoplasm of the cell. The pre-miRNA is diced by Dicer RNase and then miRNAs are incorporated into a RNA-induced silencing complex. The matured miRNA suppresses translation and transcription by uncertain mechanisms. On the other hand, nematode siRNA can be transfected into the cells, where either strand of the siRNA can bind to the RISC independently of Dicer. In the case of complementarily-paired miRNA and siRNA-to-mRNA sequences, both small RNAs induce mRNA degradation in the P-body. Human Ago1 and Ago2 are localized in the P-body and associated with GW182. The N-terminal GW182 protein can interact with the PIWI domain of Ago1. Ago2 also localizes with the decapping enzyme Dcp1 for matured mRNA and the helicase Dhh1. mRNA degradation by siRNA can be performed by the exoribonuclease Xrn1. But usually miRNA is uncomplementarily paired to the 3’ UTR of target mRNA; therefore, miRNA is believed not to destroy mRNA. (b) A schematic representation of three miRNA sources in relation to the human genome. Twelve, 9 and 43 miRNAs in the KSHV (DNA virus), HIV-1 (RNA virus) genome, and human 14q32 chromosome, respectively, are represented by the gray arrows. Protein coding regions are represented as the gray bars. Ten miRNAs (1-9 and 11) of KSHV reside in the non-coding region and two (K12-10 and 12) are within the kaposin gene. Two miRNAs (MIRH1 and MIRN367) of HIV-1 were cloned and expression was detected by northern blotting. Two (TAR-3p and 5p) were observed with the artificial bio-assay and are involved in the secondary structured TAR region. Five (#1-#5) were predicted by the computing analysis. The sequences of miR-#4 is partially overlapped into those of miR-N367. Two viral siRNAs (vs iRNA#1 and #2) were detected by computation and northern blotting. The type I retrotransposon RTL1 is involved in the imprinted chromosome region. Five miRNAs (miR-127, miR-136, miR-431, -432, and -433) in the RTL1 gene were isolated. The antisense RTL1 transcript is maternally expressed, and it was initially reported in an ovine model as anti-PEG11. The maternal expression of the antisense transcript suggests to be controlled by these miRNAs.