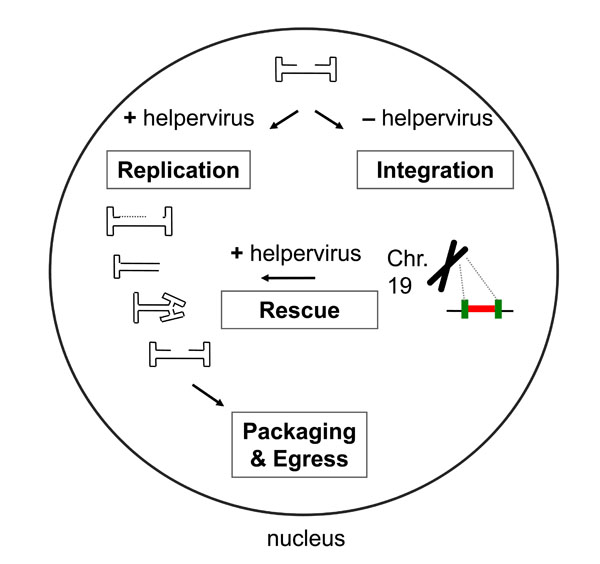
Fig. (4) The life cycle of AAV. Co-infection of AAV and helpervirus, adenovirus or HSV-1, leads to viral gene expression, viral DNA replication, and production of progeny virus. In the absence of helpervirus, the genome of AAV can integrate into a specific site on human chromosome 19. In the presence of helpervirus, integrated AAV genomes are rescued and enter the lytic replication cycle.