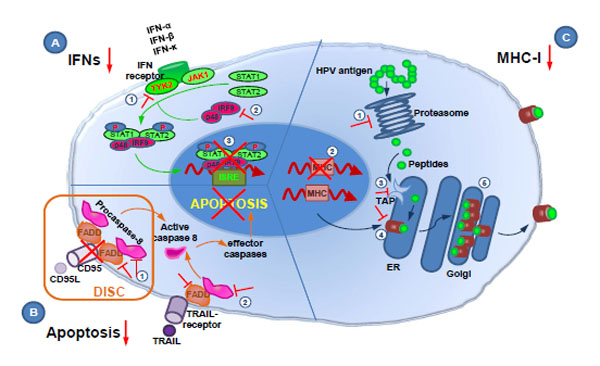
Fig. (1) Intracellular HPV immune evasion mechanisms. (A) HPV dysregulates the interferon response via interaction with the TYK2 kinase
(1) and the p48/IRF9 complex (2), thus inhibiting the formation of the ISGF3 transcription complex that binds ISRE in the nucleus (3). (B)
HPV promotes apoptosis resistance through down-regulation of the CD95 receptor on the cell surface and modulation of the DISC formation
(1), and by degradation of the pro-apoptotic molecules FADD and procaspase-8 (2). (C) HPV causes reduction of antigen presentation by
down-regulation of the antigen processing machinery via inhibition of expression of proteasome subunits (1), MHC class I (2), TAP (3), and
reduction of MHC-I trafficking by direct interaction with the MHC-I heavy chain (4) and arresting of MHC-I molecules in the Golgi
apparatus (5).