- Home
- About Journals
-
Information for Authors/ReviewersEditorial Policies
Publication Fee
Publication Cycle - Process Flowchart
Online Manuscript Submission and Tracking System
Publishing Ethics and Rectitude
Authorship
Author Benefits
Reviewer Guidelines
Guest Editor Guidelines
Peer Review Workflow
Quick Track Option
Copyediting Services
Bentham Open Membership
Bentham Open Advisory Board
Archiving Policies
Fabricating and Stating False Information
Post Publication Discussions and Corrections
Editorial Management
Advertise With Us
Funding Agencies
Rate List
Kudos
General FAQs
Special Fee Waivers and Discounts
- Contact
- Help
- About Us
- Search

The Open Electrical & Electronic Engineering Journal
(Discontinued)
ISSN: 1874-1290 ― Volume 13, 2019
Minimum Delay Congestion Control in Differentiated Service Communication Networks
Saadi Alobaidi Khodhair, Majid S. Naghmash*, Riyadh Bassil Abduljabbar, Ali Amer Ahmed ALRawi
Abstract
Introduction:
This paper presents a minimum delay congestion control in differentiated Service communication networks. The premium and ordinary passage services based fluid flow theory is used to build the suggested structure in high efficient manage. The established system is capable to adeptly manage both the physical network resource limitations and indefinite time delay related to networking system structure.
Methods:
The effectiveness of the suggested congestion controller system is demonstrated with mathematical consequences in formal framework by using modified sliding controller (MSMC) techniques. This technique provides high utilization and less delay after adapting the state feedbacks controllers with sliding mode controller. The Quality of Service (QoS) requirements in term of effective and dynamic regulation of network resources have been achieved in the existing design.
Results:
The capacity and bandwidth limitations are considered as a restriction on the input of network. The results of this approach are developed and compared with a conventional design.
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2018Volume: 12
First Page: 42
Last Page: 51
Publisher Id: TOEEJ-12-42
DOI: 10.2174/1874129001812010042
Article History:
Received Date: 12/4/2018Revision Received Date: 9/7/2018
Acceptance Date: 10/7/2018
Electronic publication date: 31/07/2018
Collection year: 2018
open-access license: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC-BY 4.0), a copy of which is available at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
* Address correspondence to this author at the Iraqi Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Dijlah University College, Baghdad, Iraq; Tel: +9647812326878; E-mail: Majid.salal@duc.edu.iq
| Open Peer Review Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manuscript submitted on 12-4-2018 |
Original Manuscript | Minimum Delay Congestion Control in Differentiated Service Communication Networks | |
1. INTRODUCTION
The importance of commercial and military applications increased more and more in researcher thinking to find efficient and reliable communication systems. To realize and achieve the tasks over a large area, the exchanges are required with a number of geometrical components distribution [1G. Sangeetha, M. Vijayalakshmi, S. Ganapathy, and A. Kannan, "A Heuristic path search for congestion control in WSN", Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Springer, vol. 11, pp. 485-495.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3953-9_47] ]. The communication network system with technical development entrenched have been coming to such components and processing capabilities as well as activating and sensing of communication capabilities. Usually, these type of devices are referred to intelligent agents, which is known as an independent unit and performances activity to provide the target requirements [2X. Yang, Consensus congestion control in multirouter networks based on multiagent system, Hindawi Complexity, .].
The intelligent agent’s degree in specific domain leads to the capability of learning and reasoning which is required to have knowledge base access and interference engine to determine the performance of an agent in the sense which successfully grips novel responsibilities [3Z. Ning, F. Xia, and N. Ullah, "Vehicular social networks: Enabling smart mobility", IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 16-55.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600263] ].
The intelligent agent’s mobility has to move from the destination point to carry out the job responsibility and not restricted. This will have a certain degree of mobility in this case. Furthermore, the advantage of mobility conditions is to have representative’s functionality after the position invented from the disconnected case. By mean of multi-Agent systems, the intelligent agents are capable of arranging all the agents in case of exit from the distributed way and communicate over networks by using two monitors with control environments. These type of systems have a challenge in agents capability which must be capable of perceiving, reasoning and evolving with their situation and collaborated with other nodes to realize widespread system purposes [4M Xiang, and Qin Qu, "A congestion control strategy for power scale-free communication network", Appl. Sci. J., . October]. The Multi-Agent Systems are able to overcome the difficulties for individual agent, which provide suitable solutions in the old systems. To develop the Multi-Agent System, each one is respected as only node, which may consist of numerous instruments, decision maker and actuator. To make a decision and receive information freely, the data exchange process should cooperate with all nodes. The Multi-agent systems have to review a sensor and make a decision in the network and actuated too. The data collected from environments by the sensor and perform actions in the system actuators has been done normally with extremely mobility with energy resources processor and memory to provide the decision making [5D.O Dike, V. Obiora, and C Eze, "Improving congestion control in data communication network using queuing theory model", Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 49-53.]. The fast growth in internet field for voice and video applications is lead to finding an efficient construction in internet networks with efficient congestion control algorithms in order to provide more demand to the user nowadays [6W. Chen, "Joint QoS provisioning and congestion control for multi-hop wireless networks", EURASIP J. on Wireless Communi. Network., .
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0519-2] ]. Therefore, the suggested differentiated services were designed to carry the Quality of Services (QoS) in TCP/IP network [7Sanyam Agarwal, and Tulika Kansal, "Congestion control schemes in ATMNetworks for ABR services: An Overview", I.J. Electron Infor Eng., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 57-67. Dec]. In the networks, the congestion control still has a crisis, which needs to look for high-performance idea. Numerous efforts have been proposed to improve the congestion controller by using linear control scheme [8Akshay Mishra, and Nirmala Sinha, "Congestion control issues & trends", Int. J. Adv. Res. Comp. Sci. Software Eng., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 798-802. April
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0519-2] -12Ali A. Ahmed, RB Ahmad, A. Yahya, H H. Tahir, and J. Quinlan, "Variable structure system with sliding mode controller", Procedia Eng., vol. 53, pp. 441-452.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.02.058] ].
In spite of these efforts, the congestion controller architecture whose performance could be logically recognized and established in repetition is motionless interesting unsettled problematic [13R. Jain, "A congestion control system based on VANET for small length roads", Ann. of Emerging Technol. in Comput., vol. 2, no. 1, . [AETiC].]. In this paper, the design of a robust dynamic system called Modified Sliding Mode Controller (MSMC) has been used to provide high utilization, less delay, while the network fulfills with the demands of each traffic flow. Flexible MSMC theory is used to compensate the congestion controller in proposed design and implementation.
2. DYNAMIC NETWORK MODEL
This subdivision presents the equation of state space system for the M / M/ 1 line. An extension to consider the delay in traffic includes uncertainty in the models. Subsequently, three groups of passing utilities have projected into the networks. Fig. (1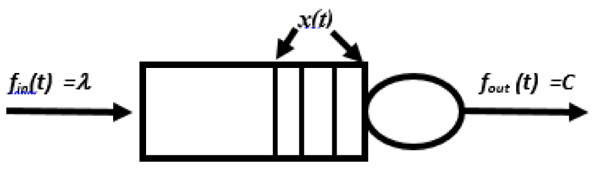 ) illustrates the model of fluid flow assuming that x (t) is a changeable condition representing the standard numeral of the set in the system illogically at matching period with the time (t). In addition, fin (t) and fount (t) let are composed of regular incoming and leaving flow of the system, individually.
) illustrates the model of fluid flow assuming that x (t) is a changeable condition representing the standard numeral of the set in the system illogically at matching period with the time (t). In addition, fin (t) and fount (t) let are composed of regular incoming and leaving flow of the system, individually.
 |
Fig. (1) Virtually block of model line. |
The model formula of this model type is:
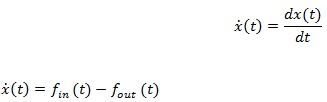 |
(1) |
In a queuing system if using equation 1, we can define the parameters of C and λ as expiration server ability and average coming rate. Assume the queue capacity is boundless, fin(t) is impartial the λ is arrival rate. The flow out of the system, fout(t), the ensemble normal employment can be related to the queue ρ(t), by fout(t)=ρ(t)C. The link of ρ that consumption can be expected by the estimated function G(x(t)) signifies together the normal link consumption at time t as a state variable function. Therefore, the queue model is represented by the following differential equation (nonlinear) [14A. A. ALRawi, S. Alobaidi, and S. Graovac, Robust adaptive gain for suppression of chattering in sliding mode controller, international conference on control robotics society, 2017.].
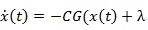 |
(2) |
The G(x(t)) function governs queuing organization. If arithmetical data is obtainable, a function G(x(t)) can be expressed empirically. Yet, it is not usually situation function of G(x(t)) it is typically resolute by the equivalent of the steady state queuing results equation (2). M / M / 1 was implemented in several traffics of communication network. These prototypical rates of input and service mutually have PDF (Poisson Distribution Function) for the state space equation M/M/1 [15D. Shen, "Congestion control and traffic scheduling for collaborative cro wdsourcing in SDN enabled mobile wireless networks", Hindawi Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput., vol. 2, .]:
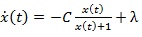 |
(3) |
A number of researchers proved the model validity of equation (3) [16W. Zhang, "The study of secure congestion control for TCP in Ad hoc networks", J. of Information Security, vol. 9, pp. 25-32.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jis.2018.91003] , 17Hassan Ebrahimirad, and M.J. Yazdanpanah, "Sliding mode congestion control in differentiated service communication networks", In: International Conference on Wired/Wireless Internet Communications, WWIC 2004, 2004, pp. 99-108.].
3. CONTROLLER DESIGN AND STRUCTURE SYSTEM
Assume that a router produces three differentiated traffic classes. Collectively, out port, a controller has been explained to occupy different type's flow of traffic entering through the port. A new sliding mode controller shown in Fig. (2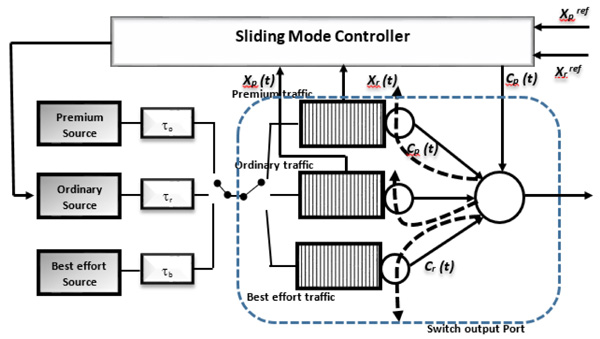 ) explained the effect of sliding controller on output signal when the input node traffic contains dissimilar traffic node. When the input node is separated from every identifier tags, headlong packets to the suitable queue to each class are in line with their class identifier tags. Hence, the maximum rate of C server in the transmit packets is given as:
) explained the effect of sliding controller on output signal when the input node traffic contains dissimilar traffic node. When the input node is separated from every identifier tags, headlong packets to the suitable queue to each class are in line with their class identifier tags. Hence, the maximum rate of C server in the transmit packets is given as:
 |
Fig. (2) The implementation of control approach. |
4. PROPOSED CONTROL APPROACH
A guaranteed exacting to delivery in premium traffic flows is needed. Packet, delay, and jitter descents should be possibly close to a certain value. The dynamic model queue can be explained in the following equation:
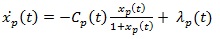 |
(4) |
To determine Cp(t) in control system network is the mean objective for whatsoever arrival rate λ p(t) and any in travel time in which the length queue, xp(t) is adjacent to a reference rate, x pref (t), quantified by the design of the system. In equation 4, xp(t) the system state can be tracked, the control signal Cp(t) resolute by the congestion controller while the disturbance is λp(t).
In order to increase extra capacity, allocating a least probable ability for the best traffic is the mean objective in this design. For this reason, it is providing a proper QoS for premium flows.
0 < Cp (t) < CserverBecause of a capacity essential, the server capacity is always less than the maximum server capacity so that a design controller constraint is further tough.
5. STRATEGY OF ORDINARY CONTROLLER
There is no limitation on the delay of ordinary traffic flows, therefore an adjustment of the capacity rates due to block controller will be specified. Assuming that, the sources send ordinary packets through the network. The dynamic model of the queue is as follows:
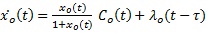 |
(5) |
Consider two important things:
- Co(t) is the residual capacity, Co (t) = Cserver - CP (t) it can be considered as disquiet to measure the premium queue in this case. In modified sliding controller, structure forces to segregate the effect of Co(t) on the variable state xo(t).
- λo is maximum value limited of λmax and non-negative λo is acceptable i.e.
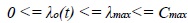 |
6. TRAFFIC OPTIMIZATION
The traffic optimization has the lowest significance and thus, it is used only in the port capacity, otherwise will not be used by the best and normal traffic flows to highlight the results. This type of service cannot be controlled.
7. PROPOSED ROBUST CONGESTION CONTROL APPROACH
An architecture DiffServ based on time-delayed robustness of congestion control clarifications remains incompetent. This paper has proposed a new algorithm categorized for example:
- The network backed congestion controller by using the queue buffer length as an information feedback.
- The future controls in the vicinity the length queue of each buffer by acting on the server bandwidth.
-
Altogether it sends back to the Ordinary source to allow maximum rate. The model of the network illustrated in Fig. (3
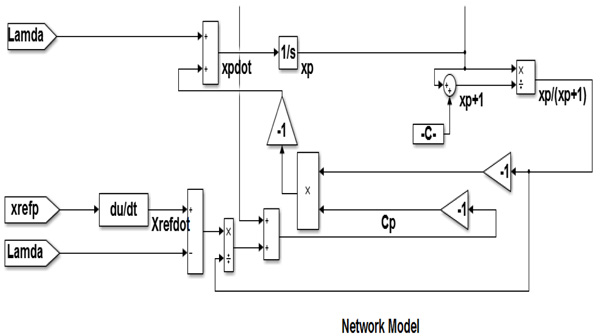 ) shows the quality of its robustness.
) shows the quality of its robustness.

Fig. (3)
The model of network.
The molds for controller design in this paper are used for the congestion control objective. Have made the following:
C max = 3,00000 Packets / Second
λ max = 15,00000 Packets / Second
There is no system delay (means τ =0). To get best and ordinary systems, two controllers are designed for both types and the sliding line of modified sliding mode controller assumes the following:
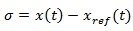 |
(6) |
Fig. (4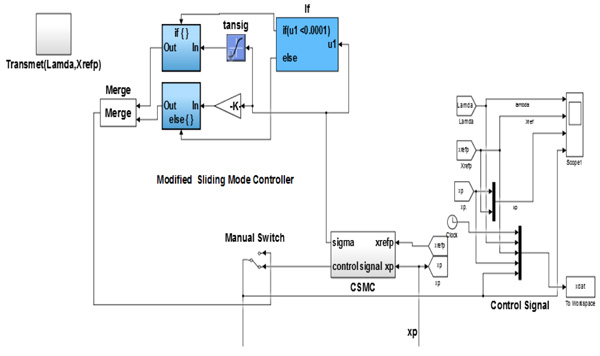 ) illustrates the proposed MSMC system with (m) and (n) input and output, respectively. To develop the design of congestion control in suggested strategy, the service framework illuminate (m) from Fig. (5
) illustrates the proposed MSMC system with (m) and (n) input and output, respectively. To develop the design of congestion control in suggested strategy, the service framework illuminate (m) from Fig. (5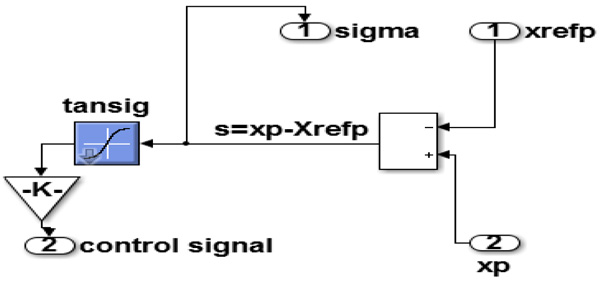 ) is used. The sliding mode of congestion controller could be expressed as follows given by the following formula which was designed in the state space error by defining the variables error.
) is used. The sliding mode of congestion controller could be expressed as follows given by the following formula which was designed in the state space error by defining the variables error.
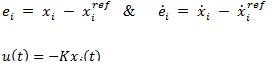 |
(7) |
Where K is a state feedback gain that can be evaluate in below gain Equation?
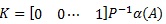 |
(8) |
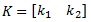 |
(9) |
To combine the sliding mode criteria with state feedback gain Equation 6 needs to be reformulated as follows:
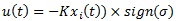 |
(10) |
by substituting Equation 8 in Equation 9
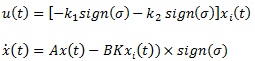 |
(11) |
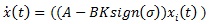 |
(12) |
Substituting Equation 11 in Equation 12
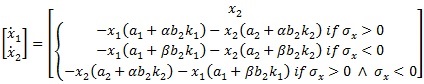 |
(13) |
 |
Fig. (4) Block diagram of the MSMC simulation. |
Fig. (5 ) shows simulation results simulation results are illustrated for premium traffic and the new sliding mode controller. Figs. (6a
) shows simulation results simulation results are illustrated for premium traffic and the new sliding mode controller. Figs. (6a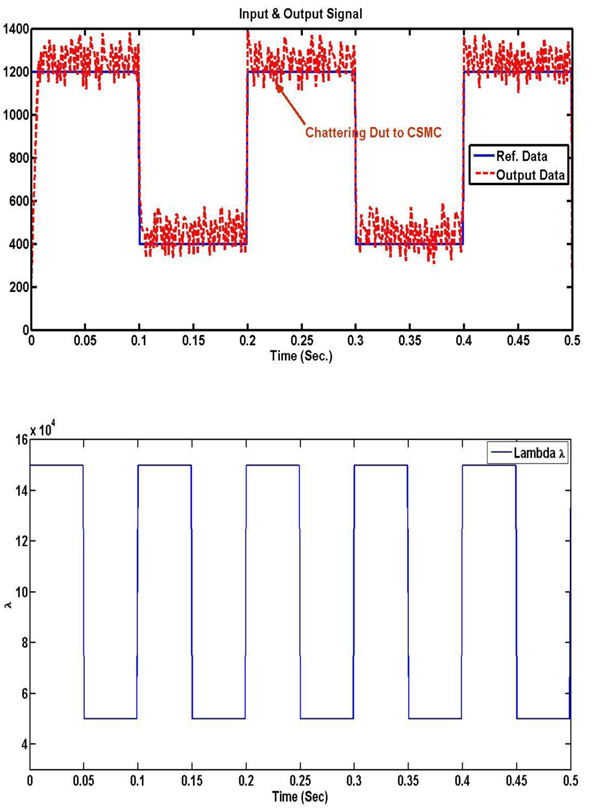 and b
and b ) shows the input and output signals, the reference data and the output data. It is clear that the proposed new sliding mode controller technique minimizes chattering effect significantly due to the reduced oscillations. Fig. (6b
) shows the input and output signals, the reference data and the output data. It is clear that the proposed new sliding mode controller technique minimizes chattering effect significantly due to the reduced oscillations. Fig. (6b ) illustrates x(t) and xref(t) for best and proposed new sliding mode controller, respectively. To achieve better rising and settling time behavior of x(t), this system has been suggested.
) illustrates x(t) and xref(t) for best and proposed new sliding mode controller, respectively. To achieve better rising and settling time behavior of x(t), this system has been suggested.
8. THE OUTPUT RESULTS
 |
Fig. (5) Simulation of sliding mode controller. |
 |
Fig. (6) xpref (t) and xp(t). |
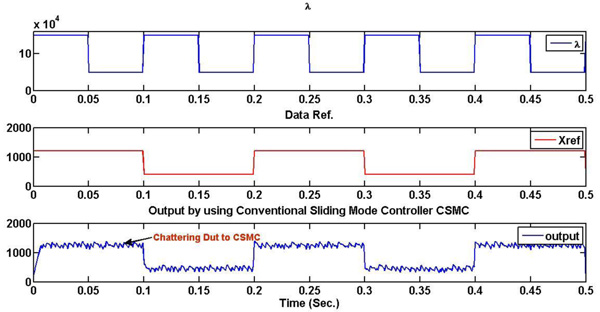 |
Fig. (7) Output rate of premium's buffer. |
Fig. (7 ) shows the output rates for the conventional sliding mode controller CSMC buffers and the output rates of Premium buffer as well. Investigation of the robustness of the proposed new sliding mode controller is done by applying the uncertainty and the round trip time delay for the system.
) shows the output rates for the conventional sliding mode controller CSMC buffers and the output rates of Premium buffer as well. Investigation of the robustness of the proposed new sliding mode controller is done by applying the uncertainty and the round trip time delay for the system.
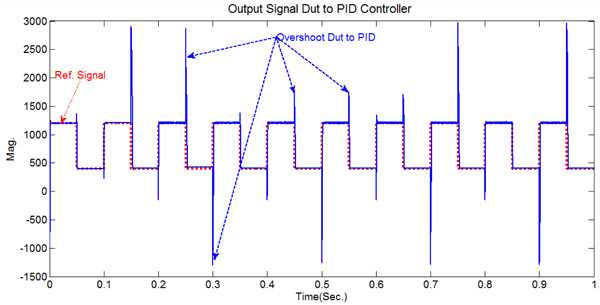 |
Fig. (8) xpref(t) and xp(t) with uncertainty and delay using PID controller. |
Fig. (8 ) shows the tracking behavior set point of xp(t) and xp. ref(t) with delay time respectively according to a functional situation which is applied. Clearly, the observation is the distortion which is caused by the overshoots due to high gain in PID controller, distorted data does not match with the data sent, these distortions appear in the data received. Although the data is highly congruent, causing data change in logical data. The comparison results from three types of controller (Conventional SM New Sliding Mode Controller and PID) illustrated in Table 1. The presentation of xp(t) in suggested sliding mode controller and the achievement of the controller does not vary changing and received dated effect as well as shown in Fig. (9a
) shows the tracking behavior set point of xp(t) and xp. ref(t) with delay time respectively according to a functional situation which is applied. Clearly, the observation is the distortion which is caused by the overshoots due to high gain in PID controller, distorted data does not match with the data sent, these distortions appear in the data received. Although the data is highly congruent, causing data change in logical data. The comparison results from three types of controller (Conventional SM New Sliding Mode Controller and PID) illustrated in Table 1. The presentation of xp(t) in suggested sliding mode controller and the achievement of the controller does not vary changing and received dated effect as well as shown in Fig. (9a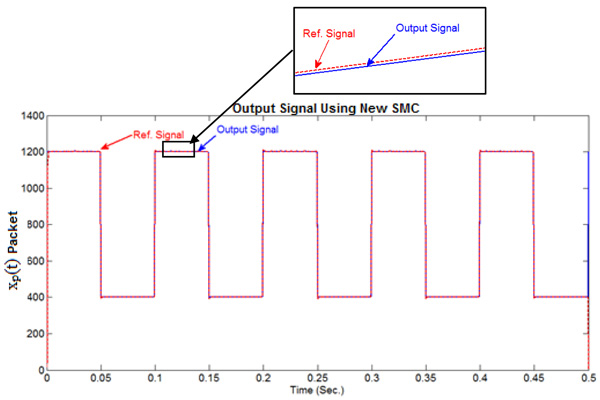 , b
, b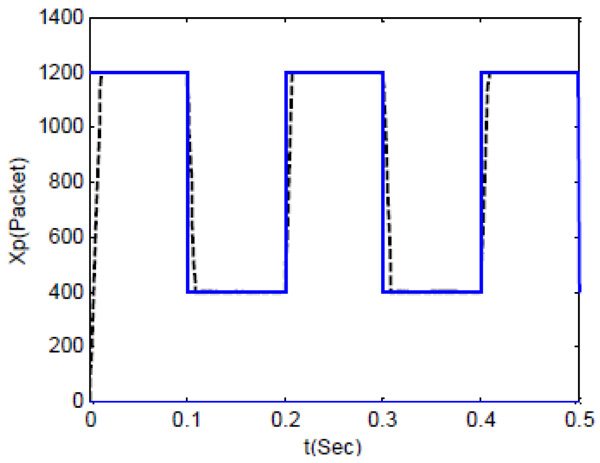 ). Consequently, the results indecision does not effect on the closed-loop system in current development. Thus, the xo(t) performance is somewhat inferior to the case of deprived delay indeed. Meaning that the suggested system has proved its robustness and significantly affected around the trip time compensating.
). Consequently, the results indecision does not effect on the closed-loop system in current development. Thus, the xo(t) performance is somewhat inferior to the case of deprived delay indeed. Meaning that the suggested system has proved its robustness and significantly affected around the trip time compensating.
 |
Fig. (9a) xpref(t) and xp(t) with uncertainty and delay using New SMC. |
 |
Fig. (9b) xpref(t) and xp(t) with uncertainty and delay using fuzzy with PID ref. [17Hassan Ebrahimirad, and M.J. Yazdanpanah, "Sliding mode congestion control in differentiated service communication networks", In: International Conference on Wired/Wireless Internet Communications, WWIC 2004, 2004, pp. 99-108.]. |
CONCLUSION
The present paper introduces new control of congestion networks by applying modified sliding mode Controller. A new sliding mode control system was proposed and Network system is modeled. The modeling of the proposed control system was based on mating between the state feedbacks controllers with sliding mode controller; it has been named MSMC. A mathematical model was derived to represent theoretical modeling in mathematical equation. The ideal model for controlling and available properties of the system state - convergence - is exploited to generate gain commensurate with the amount of error generated in the MSMC system. The differentiated-services network outline has been expected and the control approach was framed for three types of services in this paper like Premium Service and Ordinary Service as well as Best Effort Facility as a new idea. The analysis results of MSMC showed that the property and the nature of the currencies which achieved in the network system led to significantly reduce the disturbing phenomenon and delay time. These results need more tuning and developments as the future scope to minimize the delay as possible.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Decleared none.
REFERENCES
| [1] | G. Sangeetha, M. Vijayalakshmi, S. Ganapathy, and A. Kannan, "A Heuristic path search for congestion control in WSN", Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Springer, vol. 11, pp. 485-495. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3953-9_47] |
| [2] | X. Yang, Consensus congestion control in multirouter networks based on multiagent system, Hindawi Complexity, . |
| [3] | Z. Ning, F. Xia, and N. Ullah, "Vehicular social networks: Enabling smart mobility", IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 16-55. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600263] |
| [4] | M Xiang, and Qin Qu, "A congestion control strategy for power scale-free communication network", Appl. Sci. J., . October |
| [5] | D.O Dike, V. Obiora, and C Eze, "Improving congestion control in data communication network using queuing theory model", Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 49-53. |
| [6] | W. Chen, "Joint QoS provisioning and congestion control for multi-hop wireless networks", EURASIP J. on Wireless Communi. Network., . [http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0519-2] |
| [7] | Sanyam Agarwal, and Tulika Kansal, "Congestion control schemes in ATMNetworks for ABR services: An Overview", I.J. Electron Infor Eng., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 57-67. Dec |
| [8] | Akshay Mishra, and Nirmala Sinha, "Congestion control issues & trends", Int. J. Adv. Res. Comp. Sci. Software Eng., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 798-802. April [http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0519-2] |
| [9] | N. Ramanjaneya Reddy, P. Chenna Reddy, and M. Padmavathamma, Efficient traffic engineering strategies for improving the performance of TCP friendly rate control protoco, august 2017. |
| [10] | C-Y. Chu, "Congestion-aware single link failure recovery in hybrid SDN networks", in Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Annual Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, pp. 1086-1094.IEEE INFOCOM 2015, May, Hong Kong [http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/INFOCOM.2015.7218482] |
| [11] | Km. Avni Yadavand Sachin Kumar, "A review of congestion control mechanisms for wireless networks", In: Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), 2nd International Conference on, IEEE Xplore, 22 March, 2018. |
| [12] | Ali A. Ahmed, RB Ahmad, A. Yahya, H H. Tahir, and J. Quinlan, "Variable structure system with sliding mode controller", Procedia Eng., vol. 53, pp. 441-452. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.02.058] |
| [13] | R. Jain, "A congestion control system based on VANET for small length roads", Ann. of Emerging Technol. in Comput., vol. 2, no. 1, . [AETiC]. |
| [14] | A. A. ALRawi, S. Alobaidi, and S. Graovac, Robust adaptive gain for suppression of chattering in sliding mode controller, international conference on control robotics society, 2017. |
| [15] | D. Shen, "Congestion control and traffic scheduling for collaborative cro wdsourcing in SDN enabled mobile wireless networks", Hindawi Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput., vol. 2, . |
| [16] | W. Zhang, "The study of secure congestion control for TCP in Ad hoc networks", J. of Information Security, vol. 9, pp. 25-32. [http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jis.2018.91003] |
| [17] | Hassan Ebrahimirad, and M.J. Yazdanpanah, "Sliding mode congestion control in differentiated service communication networks", In: International Conference on Wired/Wireless Internet Communications, WWIC 2004, 2004, pp. 99-108. |




