- Home
- About Journals
-
Information for Authors/ReviewersEditorial Policies
Publication Fee
Publication Cycle - Process Flowchart
Online Manuscript Submission and Tracking System
Publishing Ethics and Rectitude
Authorship
Author Benefits
Reviewer Guidelines
Guest Editor Guidelines
Peer Review Workflow
Quick Track Option
Copyediting Services
Bentham Open Membership
Bentham Open Advisory Board
Archiving Policies
Fabricating and Stating False Information
Post Publication Discussions and Corrections
Editorial Management
Advertise With Us
Funding Agencies
Rate List
Kudos
General FAQs
Special Fee Waivers and Discounts
- Contact
- Help
- About Us
- Search

The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal
(Discontinued)
ISSN: 1874-110X ― Volume 12, 2018
A Novel Hybrid Method for Solving Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem
Tao Ning1, 2, Chen Guo2, *, Rong Chen2, Hua Jin1
Abstract
For the purpose of solving the flexible job-shop scheduling problem (FJSP), an improved quantum genetic algorithm based on earliness/tardiness penalty coefficient is proposed in this paper. For minimizing the completion time and the job-shop cost, a simulation model was established firstly. Next, according to the characteristics of the due in production, a double penalty coefficient was designed and a double chains coding method was proposed. At last, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified through being applied to the Kacem example and compared with some existing algorithms.
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2016Volume: 10
First Page: 13
Last Page: 19
Publisher Id: TOCSJ-10-13
DOI: 10.2174/1874110X01610010013
Article History:
Received Date: 18/2/2015Revision Received Date: 18/9/2015
Acceptance Date: 19/9/2015
Electronic publication date: 25/3/2016
Collection year: 2016
open-access license: This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 4.0 International Public License (CC BY-NC 4.0) (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode), which permits unrestricted, non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the work is properly cited.
* Address correspondence to this author at the College of Information Science and Technology, Dalian Maritime University, China; Tel/Fax: 8613940901029; E-mail: daliannt1@126.com
| Open Peer Review Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manuscript submitted on 18-2-2015 |
Original Manuscript | A Novel Hybrid Method for Solving Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem | |
1. INTRODUCTION
Flexible Job-shop Scheduling Problem (FJSP) is the extension of Job-shop Scheduling Problem (JSP). Because FJSP can break the limit of the machines and the fixed process route, it is closer to the actual production. Thus, it is adopted more widely than the common JSP in production. The domestic and foreign scholars have studied FJSP with various methods and achieved corresponding results. FJSP was proposed by Bucker and Schlie [1P. Bucker, and R. Schlie, "Job-shop scheduling with multi-purpose machines", Computing, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 369-375, 1990.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02238804] ] in 1990. Falkenauer and Bouffoulx [2J.G. Qi, G.R. Burns, and D.K. Harrison, "The application of the parallel multi-population genetic algorithm to dynamic job shop scheduling", International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 16, pp. 609-615, 2000.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001700070052] ] studied the heterogeneous vehicle routing problem with genetic algorithm, a novel crossover operator was applied to the coding to obtain optimal solution. Reeves [3B.I. Weihong, H. Ren, and Q. Wu, "A new elitist strategy in genetic algorithm", Journal of Zhejiang University, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 32-35, 2006.] used the genetic algorithm to solve the optimal scheduling in the flow shop. The experimental results show that the genetic algorithm is better than the simulated annealing algorithm in the complicated situation. Murata [4T. Ning, C. Guo, and R. Chen, "A novel method for dynamic vehicle routing problem", Open Cybernetics & Systemic Journal, vol. 9, no. 15, pp. 1-5, 2015.] proposed a novel genetic algorithm to minimize the production style, minimize the total delay time and flow time for solving the FJSP in the flow shop. Huang Ming [5T. Ning, R. Chen, C. Guo, and L. Xu, "A scheduling strategy for dynamic vehicle routing problem based on double chains coding", Operations Research Transactions, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 72-83, 2015.] studied the parallel machine scheduling problem with process constraint. Xiong Hegen [6Q. Liu, C. Zhang, Y. Rao, and X. Shao, "Flexible job-shop scheduling problem with improved genetic algorithm", Industrial Engineering and Management, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 59-66, 2009.] solved the Dynamic Job-Shop Scheduling with the concept of generalized correlation between processes. Xie Zhiqiang [7T. Ning, "Study of Application of Hybrid Quantum Algorithm in Vehicle Routing Problem", thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, 2013.] proposed a novel scheduling algorithm. It identified the key route through decomposing the product processing tree for the method, and the product processing tree is segmented according to the fork point process. Although the above intelligent algorithms for solving job-shop scheduling problem are simple and robust, there are some shortcomings such as premature convergence and easy to fall into local optimum. Besides, the analysis and comparison of convergence about the factors influencing the result are not enough. Considering the disadvantages of the existing algorithms, this paper proposes an improved double chains quantum genetic algorithm (IDCQGA) on the basis of the research on particle swarm algorithm. Firstly, the paper establishes a multi-objective FJSP mathematical model according to different constraints. Secondly, the paper analyzes the quantum state vector and state vector superposition, then puts forward the chaotic local optimization strategy and improved method of quantum rotating angle to make up for the disadvantages of weak local search ability and premature convergence in the late. At last, the simulation results of four classical JSP and instance demonstrate that the proposed novel method can improve the efficiency of iterative search and obtain more non-dominated solutions than the existing algorithms.
2. MODEL OF FUZZY MULTI-OBJECTIVE FJSP
2.1. Problem Description
FJSP is described as follows: there are N workpieces to be processed and M machines in workshop, each workpiece i(i ε ({1,2,N}) includes ni (ni >= 1) processes, and the process should be processed with the specified route. Rij means the jth(j ε {1,2,… ni}) process of workpiece i, Mij(Mij ⊆ {1,2… ,M}) means the machine set, each Rij may be processed by any machine m(m ε {1,2…,Mij}) with processing capacity, and m can process different workpieces [8J. Zhang, W. Wang, X. Xu, and J. Jie, "Hybrid particle-swarm optimization for multi objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem", Control Theory & Applications, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 30-37, 2012.]. The performance of different machines m makes the completion time different for Rij.
2.2. Objective Function
The objective of FJSP is to select the suitable machine for each process and determine the optimum processing sequence, so that it can minimize the earliness/tardiness. If the workpiece is completed ahead of schedule in fuzzy FJSP, it can lead to the increasing of inventory cost and the delay for other workpieces. The objective function is established as follows:
To minimize the maximum completion time:
 |
(1) |
 |
(2) |
To minimize machine load:
 |
(3) |
To minimize total cost:
 |
(4) |
 |
(5) |
In formula (1), F means the total completion time of all the machines, which acts as an important index to measure the machine load. In formula (2), Fm means the total completion time of machine m, bijm means the start time of Rij in m, tijm means the processing time of Rij in m, Sijm takes the value of either 1(processed in machine m) or 0(not). In formula (3), f3 means the total load of all the machines. In formula (4), C means the total costs of workpiece i, Mi means the commodity cost of workpiece i, Cijm means the processing cost of Rij in m. In formula (5) µijm, Vijm and mean the labor cost and machine cost of Rij in m respectively.
2.3. Constraint Conditions
2.3.1. Process Constraint
The sequence constraint in the same workpiece, where Sijm= Si(j-1)m=1:
 |
(6) |
2.3.2. Machine Constraint
The same machine can only do one process at the same time, that is to say,
 if at the moment of t, then there mustn’t be Sxym=1.
if at the moment of t, then there mustn’t be Sxym=1.
2.3.3. Continuity Constraint
Rij can’t be interrupted in the processing, in formula (7), cijm means the completion time of Rij.
 |
(7) |
2.4. Description of Fuzzy Delivery
Assuming the fuzzy number
 is the convex normal fuzzy set on the real axis R, fuzzy number
is the convex normal fuzzy set on the real axis R, fuzzy number
 needs to meet the following two conditions:
needs to meet the following two conditions:
 (1) is the convex fuzzy set in the domain X; (2)
(1) is the convex fuzzy set in the domain X; (2)
 , m1 < m2.
, m1 < m2.
The trapezoidal fuzzy number
 means the fuzzy delivery of the workpiece.
means the fuzzy delivery of the workpiece.
is described as formula (8):
 |
(8) |
µ(ti) imposes the completion time satisfaction of the workpiece i.
3. IMPROVED QUANTUM GENETIC ALGORITHM
Quantum genetic algorithm (QGA) realized the diversity and parallelism of the population through replacing the chromosome coding with quantum bits probability amplitude and searching with the quantum gates. This paper proposed improved double chains quantum genetic algorithm (IDCQGA) because of there being shortcomings of complex encoding and decoding with QGA.
3.1. Improvement of Quantum Rotation Angle
The improved quantum rotation angle is divided into two parts which are deflection and direction of rotation. The data of each qubit is as follows: f(xi) says the fitness of quantum individual xi, wij says the angle of probability amplitude, K1, K2,…, Kn say the first n elite individual with the highest fitness in the current state, wn0j says the jth qubit angle of the nth elite individual. The paper proposed an improved method for the rotation angle of qubit combining the chaos theory. The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Initialize the parameters. Make j=1 and generate the initial value by the Logistic equation;
Step 2: Calculate the direction of the rotation angle. K1 says the optimal elite individual and meets
 , the direction of the rotation is shown in formula (9):
, the direction of the rotation is shown in formula (9):
 |
(9) |
sgn() says the symbol function, αi,jβi,j say the probability amplitude of the jthqubit, K1j says the value of the jth qubit in K1;
Step 3: Calculate the deflection of the rotation angle guided by the elite quantum;
Step 4: Calculate the chaos perturbation of the qubit, i.e.
 |
(10) |
Step 5: Calculate the rotation angle of the qubit, and the positive or negative value is decided by the direction of rotation, i.e.
 |
(11) |
Step 6: Judge whether the calculation for the qubit is completed, if the calculation is not completed, it will make j=j+1 and turn to Step 2.
3.2. Chaotic Local Search Strategy
Chaos operator can unify the deterministic and stochastic, its criterion of quantitative is Lyapunov index.
Assume that there are an initial x0 and its adjacent point x0 + δ0 , the distance between the two points is as follows after one iteration:
 |
(12) |
and the distance between the two points is as follows after n iterations:
 |
(13) |
if n → ∞, formula (13) may change into:
 |
(14) |
λ is Lyapunov index, the larger a is, the stronger chaotic of system is. λ=0 is the bifurcation point of the system from motion state to the chaotic state.
In order to avoid falling into local optimization for the particle swarm, it will use chaotic operator to optimize the global optimal solution in each generation. The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Generate the initial chaotic variable λi0 according to Logistic, in which:

Step 2: Calculate the chaotic variable λi(t+1) of next generation;
Step 3: Change the chaotic variable λi(t+1) into xi(t+1) which is position vector and the principle of conversion is shown in formula (15),
 |
(15) |
mi and ni are constant;
Step 4: Calculate the fitness of Xi(t+1), if it is better than the current global optimal solution or has reached the maximum number of iterations, xi(t+1) should be output; otherwise, it will turn to Step 2.
3.3. Non Dominated Sorting
It is difficult to obtain the optimal solution which will meet all the objectives for FJSP. A sorting method of non dominated is proposed based on the fuzzy theory, and the method realizes the classification depending on the parameters Np and np of individual p in population S, the specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Initialize the parameter set Np which includes all the individuals dominated by p and make Np= Ø
Step 2: Initialize the variable np and np means the number of individuals which can dominate p;
Step 3: Calculate dominance relationship, p, q ε S, if p can dominate q, then Np=Np U{q}, else if q can dominate p, then np=np+1; if np=0, then p is a non-dominated individual, denoted as pr=1, and p joins R1, that is to say R1=R1 U{p};
Step 4: Q means the set of residual individuals, making i=1, when Ri ≠ ∅, Q = ∅. If q ε Np, then nq= nq-1, else if nq=0, then qr=i+1; make
 , i=i+1, Ri=Q;
, i=i+1, Ri=Q;
Step 5: Judge whether Ri is empty or not, if it is empty, the calculation will stop, otherwise, it will turn to Step 4.
In order to maintain the diversity of the population, the selection is made according to the crowding distance of the chromosomes based on non dominated sorting.
D. Description of improved algorithm
Step 1: n chromosomes produced by the double chains quantum coding scheme make up the initial population;
Step 2: Decoding of the chromosome based on some constraint conditions;
Step 3: Non dominated sort and calculate crowding distance towards population;
Step 4: Solve the fitness value of each chromosome, record the contemporary optimal solution Xgb and the current optimal solution Xb;
Step 5: Execute mutation by Hadamard towards each chromosome according to mutation probability to obtain new population T;
Step 6: If it meets the conditions for convergence or has reached the maximum number of iterations, turn to Step7; otherwise adding 1 to iterations and turn to Step 2;
Step 7: Output the current optimal solution Xb and the corresponding fitness function.
4. ANALYSIS AND VERIFICATION
In this paper, the classic Kacem [9I. Kacem, S. Hammadi, and P. Borne, "Approach by localization and multi-objective evolutionary optimization for flexible job-shop scheduling problems", IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1-13, 2002.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TSMCC.2002.1009117] ] example was selected and performed 20 times with Matlab7.0 independently. Solved the three standard problems of Kacem (4 workpieces 5 machines, 10 workpieces 10 machines, 15 workpieces 10 machines) with IDCQGA and compared with existing algorithms such as AL+CGA [9I. Kacem, S. Hammadi, and P. Borne, "Approach by localization and multi-objective evolutionary optimization for flexible job-shop scheduling problems", IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1-13, 2002.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TSMCC.2002.1009117] ], PSO+TS [10Y. Wang, Y. Feng, J. Tan, and Z. Li, "Optimization method of flexible job-shop scheduling based on multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm", Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 190-196, 2011.] and IPSO [11M. Liu, Z. Zhao, and G.E. Maogen, "Online optimization for assembly quality of complex mechanical products based on improved PSO", Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 252-258, 2013.]. The result is shown in Table 1, including completion time (Tx), total load to the machines (Mt); maximum load in balancing the load of the machines (Mx). It can be known from Table 1 that the proposed IDCQGA may obtain more non-dominated solutions. The proposed penalty coefficient is not evenly distributed with the change of the delivery time, which can be obtained through the formula (10) and (11). Aiming at minimizing the process time, penalty value, machine load and total cost to optimize the objective using the propose IDCQGA. Fig. (1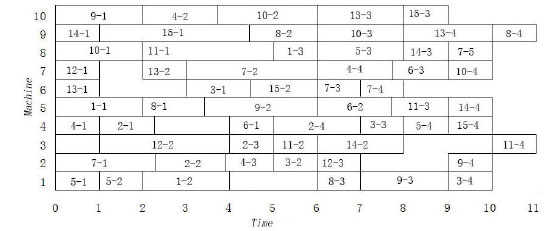 ) is the Gantt chart of the solution (10, 91, 10) in 1510 example.
) is the Gantt chart of the solution (10, 91, 10) in 1510 example.
The results in Table 2 are average value after running 50 times with IDCQGA, PSO [10Y. Wang, Y. Feng, J. Tan, and Z. Li, "Optimization method of flexible job-shop scheduling based on multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm", Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 190-196, 2011.] and IPSO. It can be known from the results that the optimal solution and average solution with the proposed algorithm are better than those of PSO, IPSO.
 |
Fig. (1) Gantt chart of solution (10, 91, 10). |
CONCLUSION
The mathematical model of multi-objective FJSP was established according to the different constraints. The coding method of double chains was proposed on the basis of initializing the machine distribution chain with the method of quasi level uniform design and heuristic initializing the process chain. The non dominated sorting strategy and crowding distance selection strategy were introduced based on the fuzzy set theory. The uniformly distributed earliness / tardiness penalty coefficient was designed. Finally, the proposed algorithm was verified to be effective through comparing with other algorithms towards Kacem example.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 51579024), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DMU No. 3132014321), the Scientific Research Project of Liaoning Education Department (No. L2014183), the Project of Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program, China (No.2014921062).
REFERENCES
| [1] | P. Bucker, and R. Schlie, "Job-shop scheduling with multi-purpose machines", Computing, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 369-375, 1990. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02238804] |
| [2] | J.G. Qi, G.R. Burns, and D.K. Harrison, "The application of the parallel multi-population genetic algorithm to dynamic job shop scheduling", International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 16, pp. 609-615, 2000. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s001700070052] |
| [3] | B.I. Weihong, H. Ren, and Q. Wu, "A new elitist strategy in genetic algorithm", Journal of Zhejiang University, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 32-35, 2006. |
| [4] | T. Ning, C. Guo, and R. Chen, "A novel method for dynamic vehicle routing problem", Open Cybernetics & Systemic Journal, vol. 9, no. 15, pp. 1-5, 2015. |
| [5] | T. Ning, R. Chen, C. Guo, and L. Xu, "A scheduling strategy for dynamic vehicle routing problem based on double chains coding", Operations Research Transactions, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 72-83, 2015. |
| [6] | Q. Liu, C. Zhang, Y. Rao, and X. Shao, "Flexible job-shop scheduling problem with improved genetic algorithm", Industrial Engineering and Management, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 59-66, 2009. |
| [7] | T. Ning, "Study of Application of Hybrid Quantum Algorithm in Vehicle Routing Problem", thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, 2013. |
| [8] | J. Zhang, W. Wang, X. Xu, and J. Jie, "Hybrid particle-swarm optimization for multi objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem", Control Theory & Applications, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 30-37, 2012. |
| [9] | I. Kacem, S. Hammadi, and P. Borne, "Approach by localization and multi-objective evolutionary optimization for flexible job-shop scheduling problems", IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1-13, 2002. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TSMCC.2002.1009117] |
| [10] | Y. Wang, Y. Feng, J. Tan, and Z. Li, "Optimization method of flexible job-shop scheduling based on multiobjective particle swarm optimization algorithm", Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 190-196, 2011. |
| [11] | M. Liu, Z. Zhao, and G.E. Maogen, "Online optimization for assembly quality of complex mechanical products based on improved PSO", Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 252-258, 2013. |





